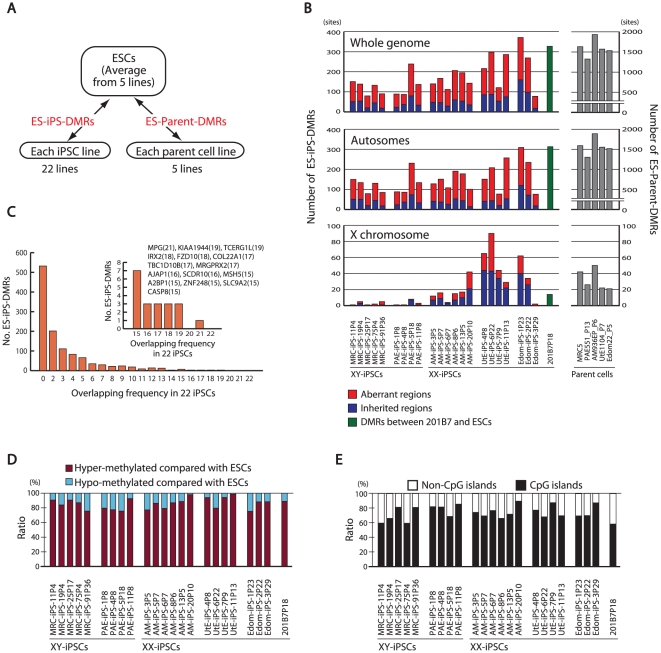
Figure 3. Aberrant methylation in human iPSCs.
(A) Comparison of DNA methylation states of each iPSC line or each parent cell line with that of ESCs. The DMRs between ESCs and iPSCs are designated as ES-iPS-DMRs, and the DMRs between ESCs and parent cells are designated as ES-parent-DMRs. (B) The number of ES-iPS-DMRs and ES-parent-DMRs on whole genome (top), autosomes (middle) and X chromosome (bottom). Ratios of number of inherited regions in iPSCs from parent cells (blue) and aberrant regions in iPSCs that differ from ESCs and parent cells (red) in the ES-iPS-DMRs are shown in bars. Female iPSCs were demonstrated to carry high number of EiP-DMRs on X chromosome. (C) Number of overlapped ES-iPS-DMRs frequency in iPSCs. No overlapping ES-iPS-DMRs in all 22 iPSC lines. (Inlet) A small number of overlapping ES-iPS-DMRs of the frequency from 15 to 22. Overlapping frequency of each gene is indicated in parentheses. (D) Proportion of the hyper- and hypo-methylated ES-iPS-DMRs. More than 75% of the ES-iPS-DMRs were hyper-methylated in iPSCs. (E) Proportion of the ES-iPS-DMRs associated with CpG islands and non-CpG islands in ach iPSC line. ES-iPS-DMRs were biased to CpG islands.