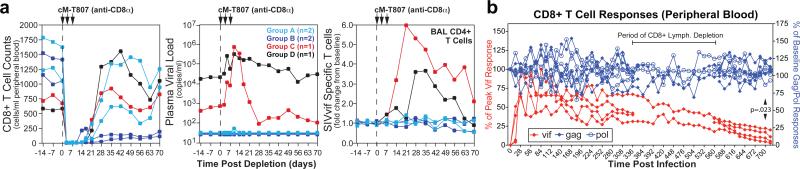
Figure 3. Immunologic characterization of long-term control associated with RhCMV/SIV vector vaccination.
a, Analysis of the effect of depletion of CD8+ lymphocytes with mAb cM-T807 on viral replication and boosting of SIVvif-specific T cell responses (in the non-depleted CD4+ subset) in 4 long-term RhCMV/SIV vector-vaccinated controllers (2 Group A and 2 Group B RM) vs. 2 conventional controllers (1 Group C, DNA/Ad5-vaccinated controller; 1 Group D spontaneous controller). b, Analysis of the frequencies of blood CD8+ T cells specific for SIV proteins that were (gag, pol) or were not (vif) included in the CMV/SIV vectors in the 4 Group A “controllers” for which long-term data is available. The response frequencies were normalized to the response frequencies immediately prior to SIV infection for the gag- and pol-specific responses, and to the peak frequencies following SIV infection for the vif-specific responses. The 4 RM used in this long-term response analysis include those subjected to transient CD4+ or CD8+ lymphocyte depletion (2 each). As Ag-specific CD8+ responses cannot be reliably determined during the period of overall CD8+ lymphocyte depletion, these periods are shown as gaps for 2 affected RM. The significance of differences in the maintenance of response frequencies of gag- and pol- vs. vif-specific CD8+ T cells in these RM was determined by Wilcoxon rank sum analysis.