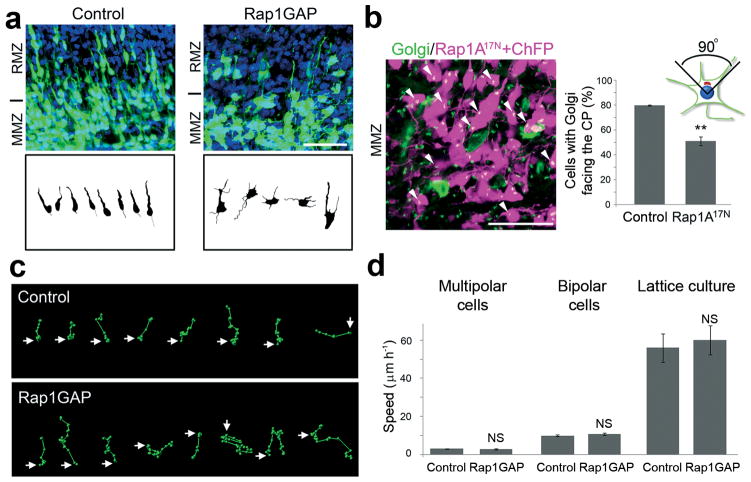
Figure 2.
Rap is required to orient multipolar cells but not for migration of bipolar neurons. The indicated plasmids were electroporated in utero at E14.5 along with plasmids expressing GFP or ChFP. (a) Computer-based reconstruction of shapes of GFP-positive neurons in E16.5 cortices at the transition between MMZ and RMZ. (b) Golgi staining (green, arrowheads) of MMZ neurons (magenta). The percentage of cells with Golgi facing the CP was calculated. (c) Tracks of migration paths followed by control and Rap-inhibited multipolar cells in the upper part of the MMZ. Positions of cell centroids in successive frames (circles) are linked by lines. The start position is marked by an arrow. (d) Migration of control and Rap inhibited GFP-positive multipolar (Control: N = 28 cells in 3 movies; Rap1GAP: N = 21 in 3 movies) and bipolar (Control: N = 121 cells in 6 movies; Rap1GAP: N = 51 in 4 movies) neurons in cortical slices prepared at E16.5 from brains electroporated at E14.5. Migration of bipolar GFP-positive cortical neurons in lattice culture (Control: N = 22 cells; Rap1GAP: N = 14). Mean + s.e.m. of average migration speed.. Scale bars, 50 μm. **, P < 0.01; NS, non significant.