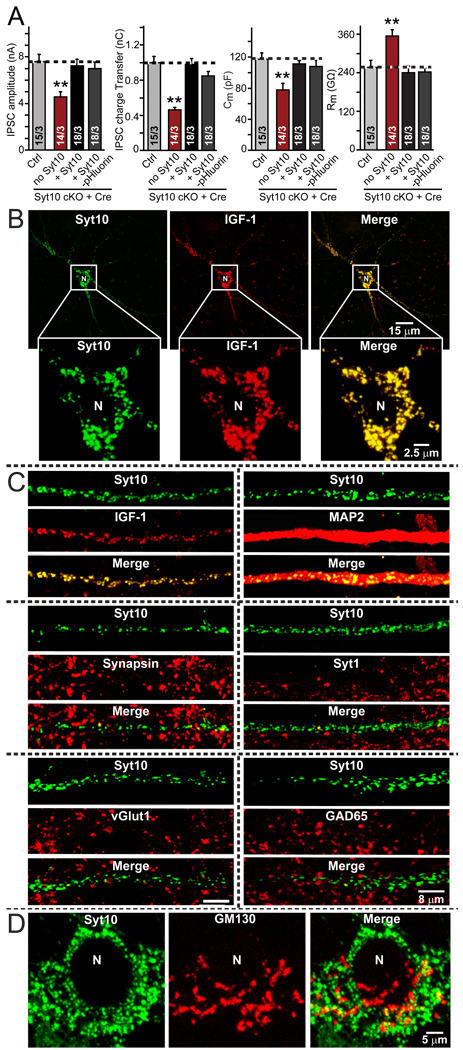
Figure 6. Co-localization of Syt10 and IGF-1 in olfactory bulb neurons.
A. pHluorin-tagged Syt10 rescues the decrease in total synaptic transmission induced by Syt10KO. Summary graphs show the IPSC amplitude (left), IPSC charge transfer (left middle), capacitance (right middle), and input resistance (right) monitored in mitral neurons from conditional KO mice infected either with control lentivirus (Ctrl) or with lentivirus expressing cre recombinase alone (no Syt) or together with untagged Syt10 or with pHluorin-tagged Syt10. Data depict means ± SEMs; number of cells and number of independent cultures analyzed is shown in individual bars. Statistical analyses were performed by Student's t-test comparing the cre-recombinase treated neurons to control neurons (**=p<0.01).
B. Low- and high-magnification images of a neuron with lentivirally expressed Syt10-pHluorin and transfected Flag-tagged IGF-1, analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence. Note complete co-localization of Syt10 and IGF-1. For demonstration that Flag-tagged IGF-1 is secreted and for an analysis of the size of the vesicles positive for Syt10 and IGF-1, see Fig. S5.
C. Analysis of the dendritic localization of Syt10 in comparison with a series of pre- and postsynaptic markers. Note the completely dendritic localization of Syt10.
D. Relative localization of Syt10 and of the Golgi-marker GM130 in the soma of a neuron to illustrate that Syt10 is not part of the Golgi apparatus.