Figure 1.
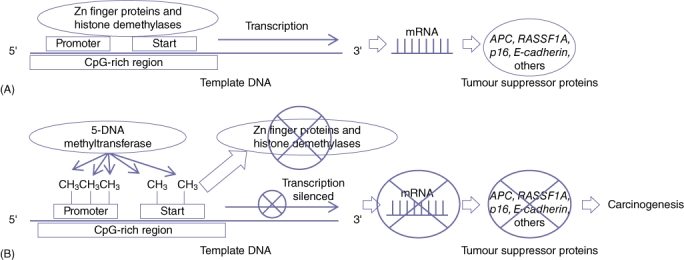
Schematic demonstrating how epigenetic DNA methylation blocks gene promoter function. (A) Areas rich in cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) are preferentially located at or near promoters of genes. Normal gene expression is promoted by zinc finger proteins (Zn fingers) and histone demethylases inhibiting methylation of the CpG sites. (B) Loss of Zn finger and histone demethylase proteins and/or increased 5-DNA methyltransferase activity results in increased CpG methylation and subsequent gene silencing. Silencing of tumour suppressor genes in this manner can lead to carcinogenesis
