Figure 6.
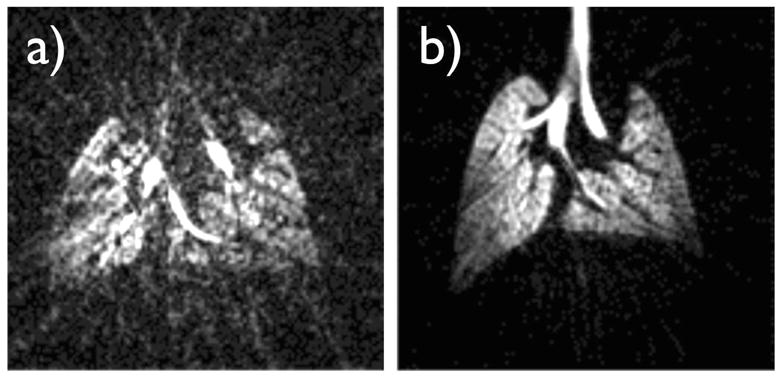
Effect of a variable tidal volume on image quality. a) A three-dimensional 3He image array of C57BL/6 mouse lungs was acquired using a respiratory gated radial acquisition over 500 breaths; the center-slice is depicted. A low driving pressure of 8.5 cm H2O was used to move hyperpolarized gas through a large diameter constrictor, which had a resistance comparable to that of the lungs. This caused the tidal volume to vary and gradually diminish over the course of 500 breaths, as the 3He supply bag depleted and became less compliant. As a consequence, the image is degraded, likely because the repositioning of the lungs was inconsistent. b) A standard high-impedance constrictor and a driving pressure of 4.5 psig were used, allowing the tidal volume to remain constant, therefore repeatedly positioning the lungs at the same location, and giving rise to a high-quality image.
