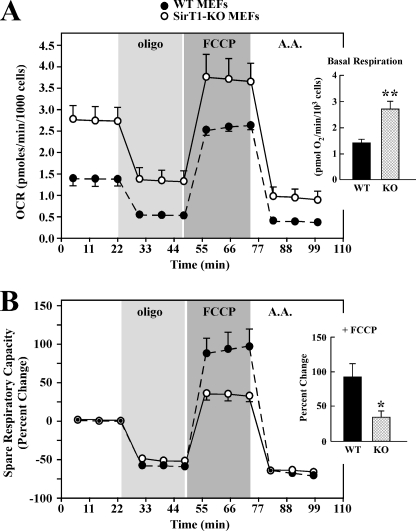
FIGURE 3.
SirT1-KO MEF cells exhibit increased basal mitochondrial respiration. Eighteen h after plating, WT and Sirt1-KO MEFs were incubated in unbuffered XF assay media in ambient air for 1 h. OCR was determined using Seahorse XF-24 metabolic flux analyzer. A, OCRs from WT cells (black) have lower basal rates of mitochondrial respiration than Sirt1-KO MEFs (open symbols). Vertical lines indicate time of addition of mitochondrial inhibitors (i) oligomycin (1 μm), (ii) FCCP (0.3 μm), or (iii) antimycin A (A.A.) (2 μm). The maximal respiratory capacity (FCCP) is significantly lower in WT than Sirt1-KO cells. Inset, average basal respiration between WT and Sirt1-KO cells. Data represent the average ± S.D. of five independent experiments. B, percent change in spare respiratory capacity in response to mitochondrial inhibitors. Spare respiratory capacity is significantly higher in WT than Sirt1-KO cells (*, p < 0.05 as compared with WT group; n = 5). Inset, average values of the spare respiratory capacity of the WT and Sirt1-KO cells after exposure to FCCP. Data represents the average ± S.D. of five independent experiments. * and **, p < 0.05 and 0.01 as compared with WT groups.