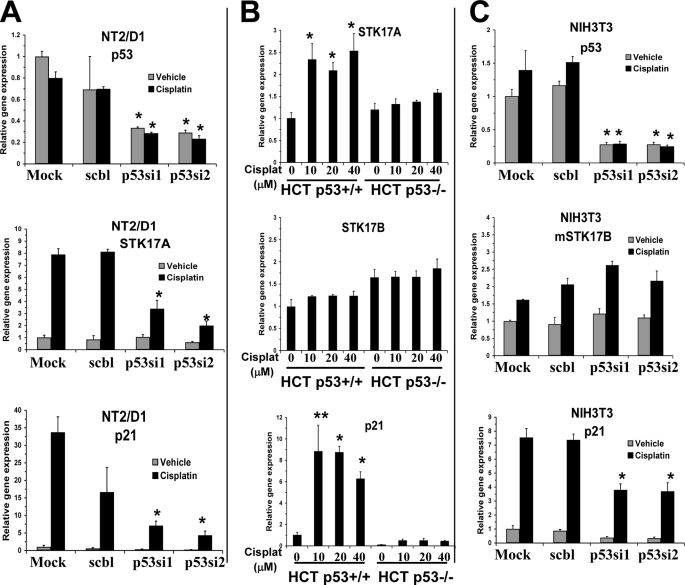
FIGURE 2.
STK17A is induced with cisplatin in a p53-dependent manner. A, cisplatin induction of STK17A in NT2/D1 cells is repressed with p53 siRNA knockdown. Expression analysis of p53 (top panel), STK17A (middle panel), or p21 (bottom panel) in NT2/D1 cells mock-transfected or transfected with either control siRNA (scbl) or two independent siRNAs targeting p53 and then treated with cisplatin for 6 h followed by real time PCR analysis 24 h later. *, p < 0.01 compared with identically treated control cells. B, STK17A is up-regulated following cisplatin (Cisplat) treatment of wild-type HCT116 cells (HCT116p53+/+) but to a much lesser extent in the isogenic p53-deleted line (HCT116p53−/−), whereas STK17B is not induced with cisplatin and not repressed in HCT116p53−/− cells. Cells were treated with cisplatin and harvested as in A for real time PCR analysis of STK17A (top), STK17B (middle), and p21 (bottom). *, p < 0.02; **, p < 0.05 compared with no cisplatin treatment. C, STK17B is up-regulated with cisplatin in a p53-independent manner in NIH3T3 cells. Expression of p53 (top panel), STK17B (middle panel), or p21 (bottom panel) in NIH3T3 cells mock-transfected or transfected with either control siRNA (scbl) or two independent siRNA targeting mouse p53 and then treated with cisplatin for 6 h followed by real time PCR analysis 24 h later. *, p < 0.02 compared with the identically treated mock control. All data points represent the average of biological triplicates. Error bars are S.D. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.