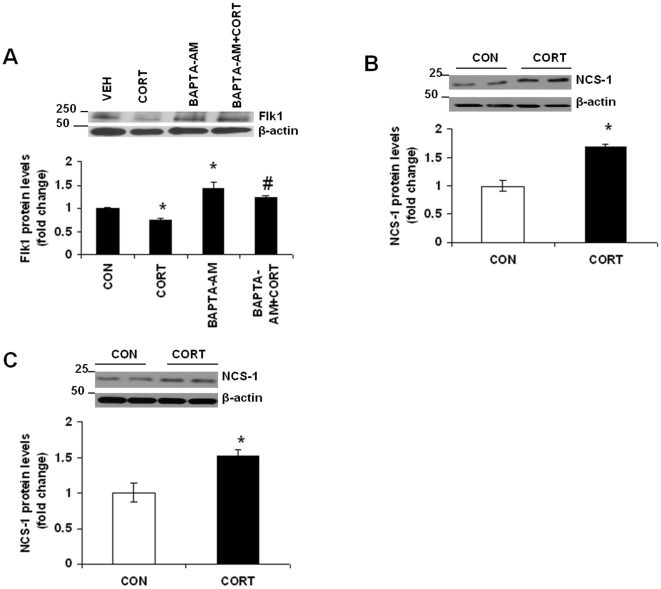
Figure 5. Chronic CORT-induced Flk1 regulation is mediated through calcium.
(A) Calcium chelator BAPTA-AM blocked CORT (CORT)-induced reduction in Flk1 protein levels. BAPTA-AM (50 µM) was applied 30 min before CORT (1 µM) treatment to cultured neurons at DIV 5. Cell lysates were collected at 48 h after CORT treatment and Flk1 protein levels were determined by western blot analysis. CON means DMSO treatment. Data represent mean±SE (n = 5) expressed as fold change in Flk1 protein levels as compared to CON. *P<0.01 versus CON; #P<0.01 versus CORT (Bonferroni's test). (B) Chronic CORT treatment increases NCS-1 protein levels in neurons. CORT (CORT; 1 µM) was applied to mouse primary cortical neurons at DIV 5. NCS-1 protein levels were determined by western blotting analysis at 48 h following CORT treatment. CON means DMSO treatment. Data represent mean±SE (n = 5) expressed as fold change in NCS-1 protein levels as compared to CON. *P<0.01 (Bonferroni's test). (C) Chronic CORT treatment increases NCS-1 protein levels in mouse frontal cortex. NCS-1 protein levels in frontal cortex of mice treated with CORT (5 mg/kg) or vehicle control (CON; 0.45% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin) for 7 weeks were determined by western blot analysis. Data represent mean±SE (n = 6) expressed as fold change in NCS-1 protein levels as compared to CON. β-actin is the loading control.*P<0.05 (Bonferroni's test).