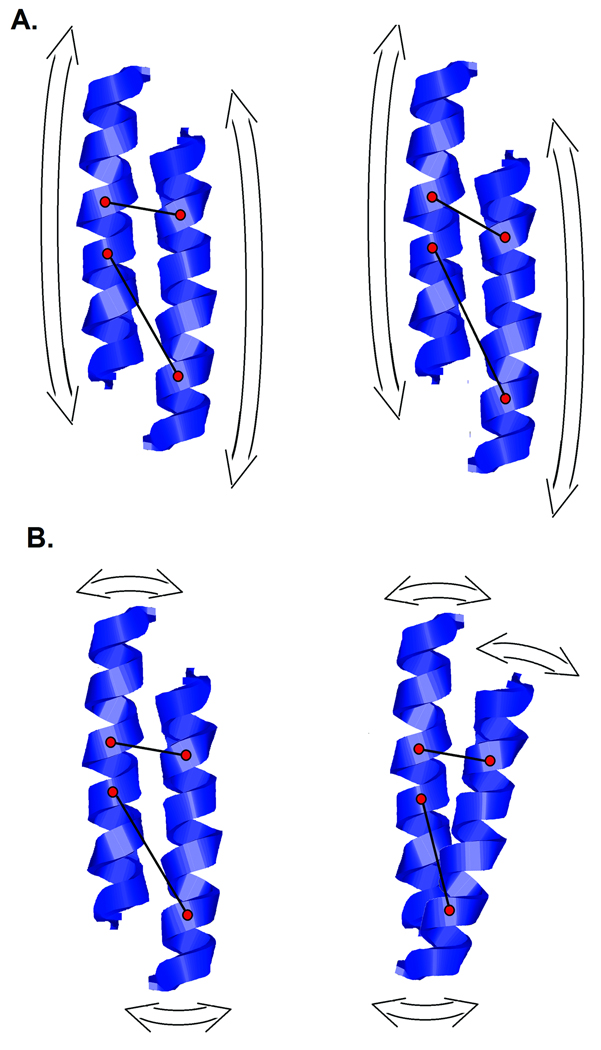
Figure 3.
Ribbon diagrams illustrating the effect of the relative motion of two α-helices on the distribution of inter-atomic vector lengths between them. (a) Translational motion will impact interatomic vectors of different lengths in different ways. Short vectors may not be greatly affected if they are nearly orthogonal to the direction motion. Longer vectors, more nearly parallel to the motion will experience greater length change. (b) Rotational motion will change the lengths of interatomic vectors with a magnitude strongly dependent on the orientation of the axis of rotation, the distance the two atoms are from that axis, and the angle between the axis and the interatomic vector.