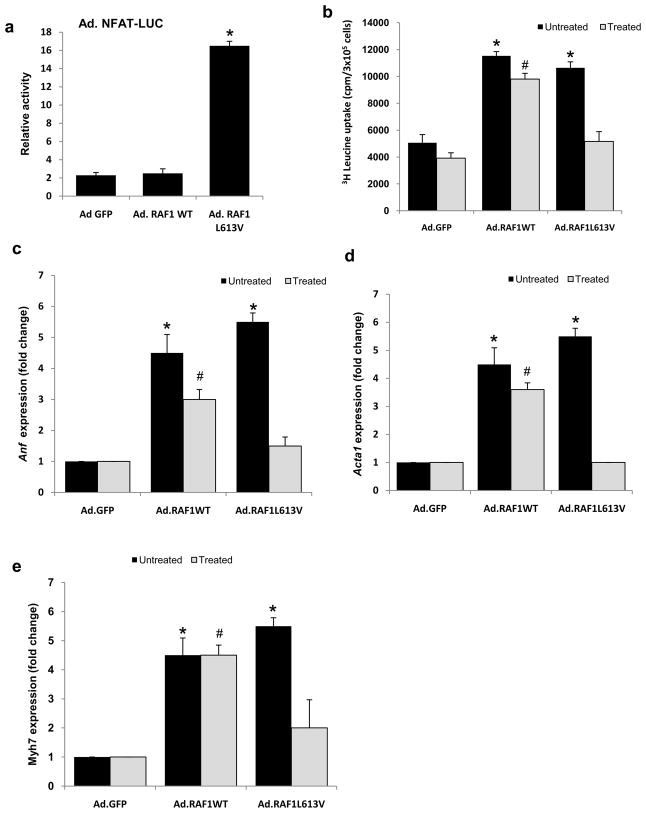
Figure 4. L613V RAF1 but not wild-type RAF1 causes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via Nfat.
(a) Nfat activity was determined in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes infected with Ad.GFP, Ad.RAF1WT and Ad.RAF1L613V along with Ad.NFAT-LUC. Luciferase activity shown as relative light units (RLU) represent mean values ± SD of three independent experiments. *P <0.001 vs Ad.GFP. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were co-infected with Ad.GFP, Ad.RAF1WT and Ad.RAF1L613V along with Ad.VIVIT (treated) that blocks NFAT specifically. Seventy-two hours hours post infection, cardiomyocytes were analyzed for protein synthesis rates (b) and steady-state mRNA levels of Anf (c), Acta1 (d) and Myh7 (e). *p <0.01 vs. untreated Ad.GFP; #p <0.01 vs. treated Ad.GFP. Mean values ± SD of three independent experiments are shown.