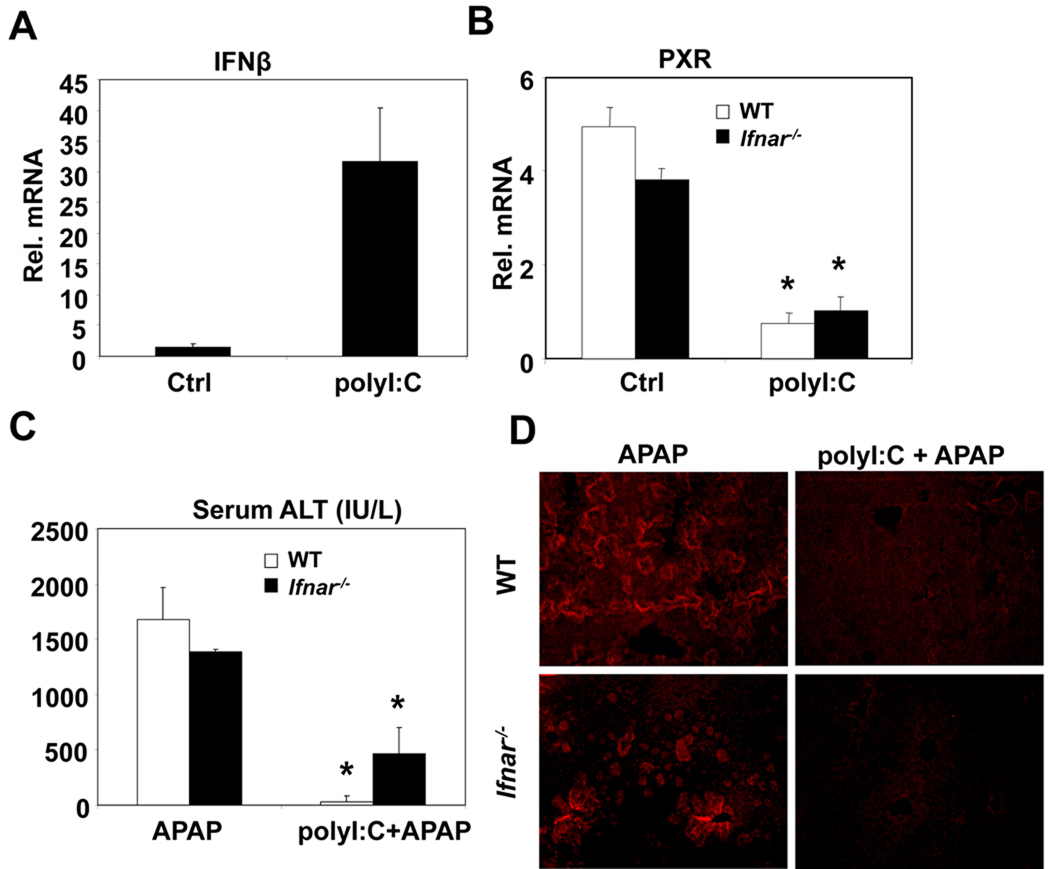
Figure 5. Involvement of Interferon and cytokines in PolyI:C protection against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity.
(A, B) Mice were treated with saline or polyI:C (100µg, i.p.). Twenty four hours post-treatment, liver RNA was isolated and analyzed by Q-PCR. (n=4, mean +/− SD, *P<0.05 compared to polyI:C untreated) (C, D) Wildtype and Ifnar−/− mice were treated with polyI:C and APAP as described above in figure 2B. Six hours after APAP administration, blood and liver samples were collected. Serum samples were analyzed for ALT levels (C) and Formalin fixed livers were indirectly stained for APAP-bound proteins (D). (n=4, mean +/− SD, *P<0.05 compared to polyI:C untreated)