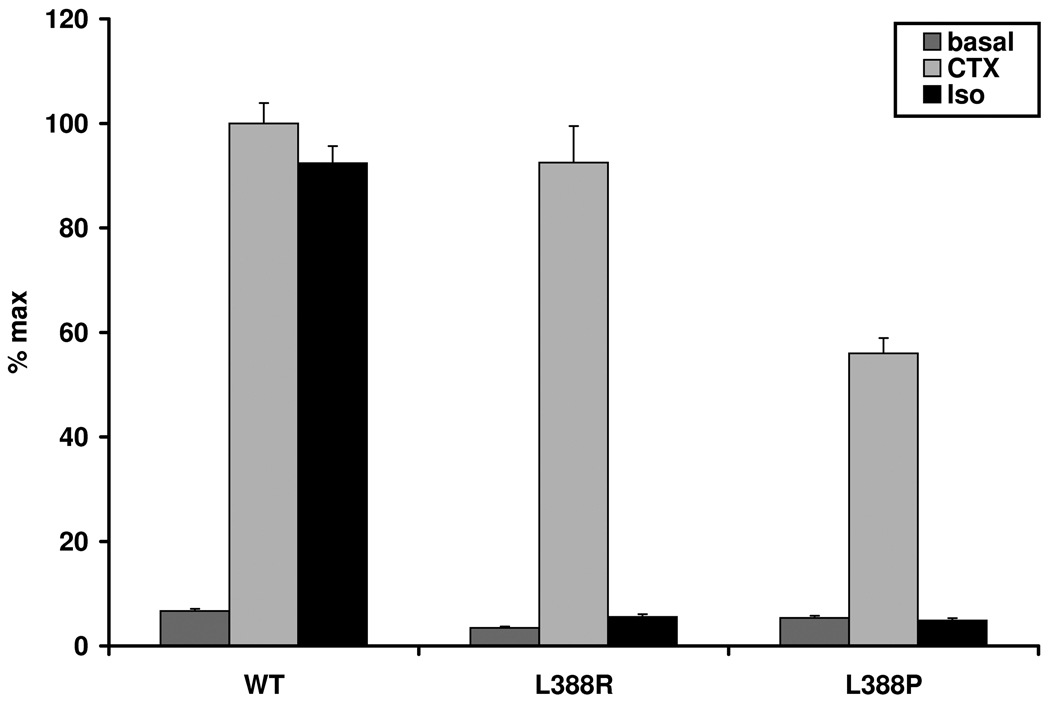
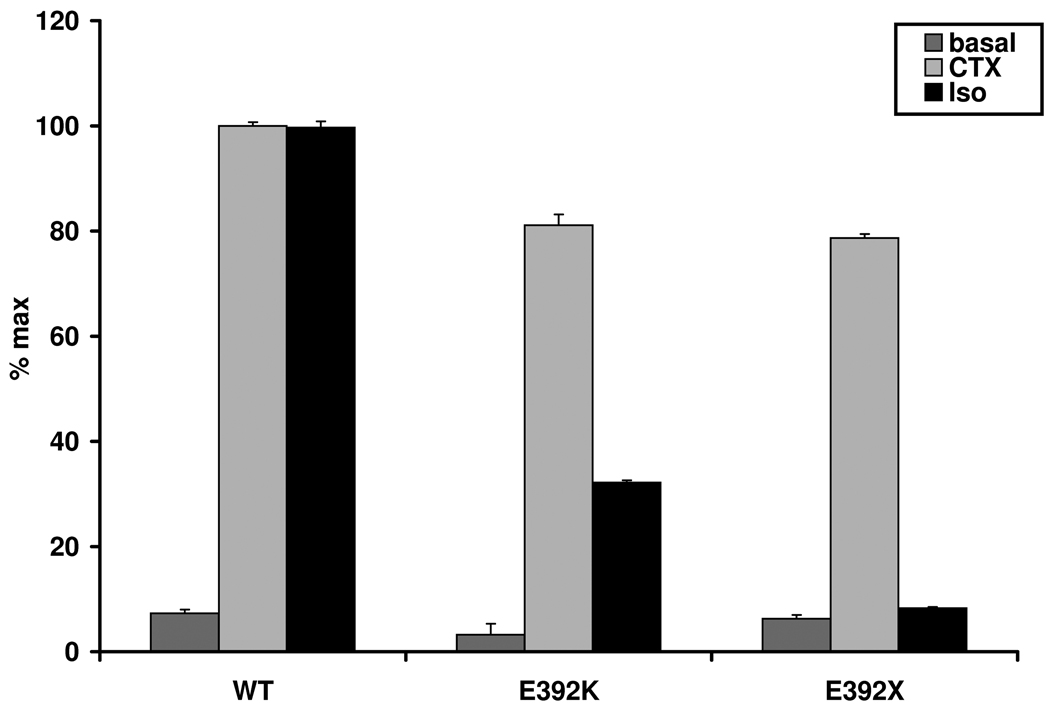
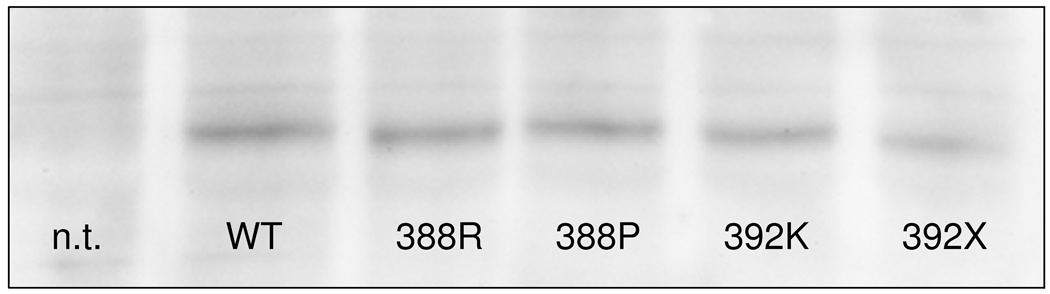
Figure 2.
PHPIc and PHPIa associated Gsα-mutants can be distinguished by in vitro stimulation tests. These experiments demonstrate that the cell model may be appropriate to reflect differences in receptor-independent activation between PHPIc and PHPIa and between the effects of missense and nonsense mutations: Panel a) In contrast to Gsα-388R, the Gsα-388P mutant found in a patient with PHPIa leads to a clearly diminished CTX induced cAMP synthesis that was significantly different from the corresponding cAMP levels in cells expressing Gsα-388R (P<0.001). Panel b) After receptor-mediated stimulation the Gsα-392K mutant revealed a residual activity that was absent in the nonsense mutant Gsα-392X (P<0.001). Panel c) Comparison of Gsα-protein levels in non-transfected (n.t.) and transfected GnasE2−/E2− cells by immunoblot analysis. Gsα-wild-type (WT), Gsα-388R (388R), Gsα-388P (388P), Gsα-392K (392K), and Gsα-392X (392X). The protein levels of the mutants were similar to those of the wild-type.