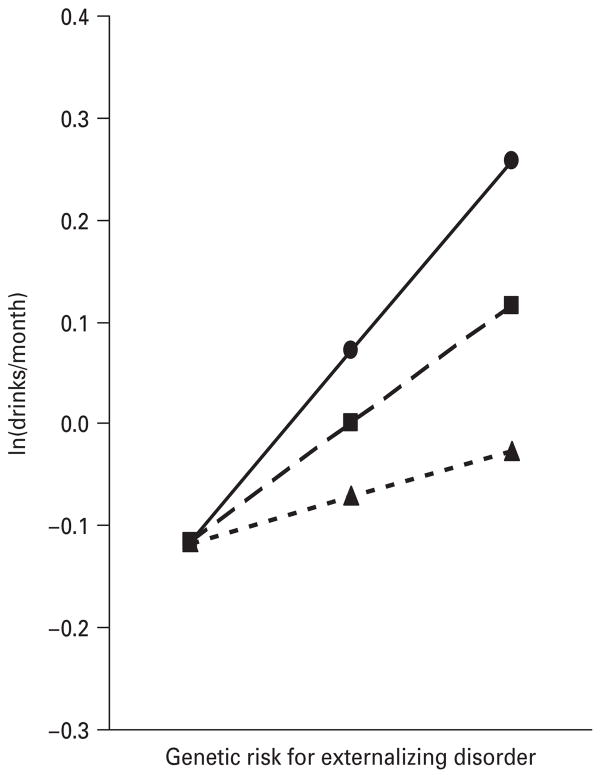
Fig. 4.
The prediction of the maximal yearly alcohol consumption from ages 12–14, as measured by standardized monthly intake, by the genetic risk for externalizing disorders (Ext Dis), level of prosocial activities (LPSA), reverse coded, and their interaction. The results, from the best-fit regression model with parameter estimates as outlined in Table 1, are depicted for three hypothetical individuals with a moderately low levels of prosocial activities [–●–, values 1 standard deviation (S.D.) above the mean], an average level of prosocial activities (– –■– –, mean value) and a moderately high level of prosocial activities (- -▲- -, values 1 S.D. below the mean).