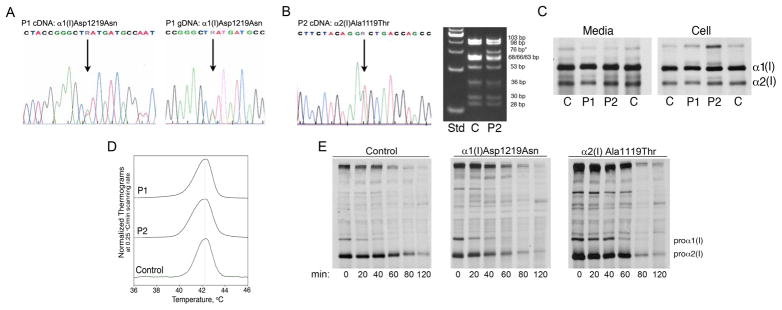
Figure 3.
Sequence and biochemistry of type I collagen. (A) Sequence tracings of Patient 1 cDNA and gDNA show the heterozygous G>A change in the α1(I) cleavage site. (B) The sequence tracing of Patient 2 cDNA shows the heterozygous G>A mutation in the α2(I) C-propeptide cleavage site (left) and a CviKI-I restriction enzyme digest of Patient 2 gDNA confirms the presence of the mutation (right). (C) The steady-state type I collagen protein from Patient 1 and Patient 2 dermal fibroblasts has slight backstreaking of the α1(I) and α2(I) chains in the cell fraction. (D) Differential scanning calorimetry reveals that the secreted procollagen of both patients has normal thermal stability. (E) A chain incorporation assay demonstrates that Patient 1 procollagen was incorporated normally into heterotrimers, while the incorporation of Patient 2 procollagen was only slightly delayed.