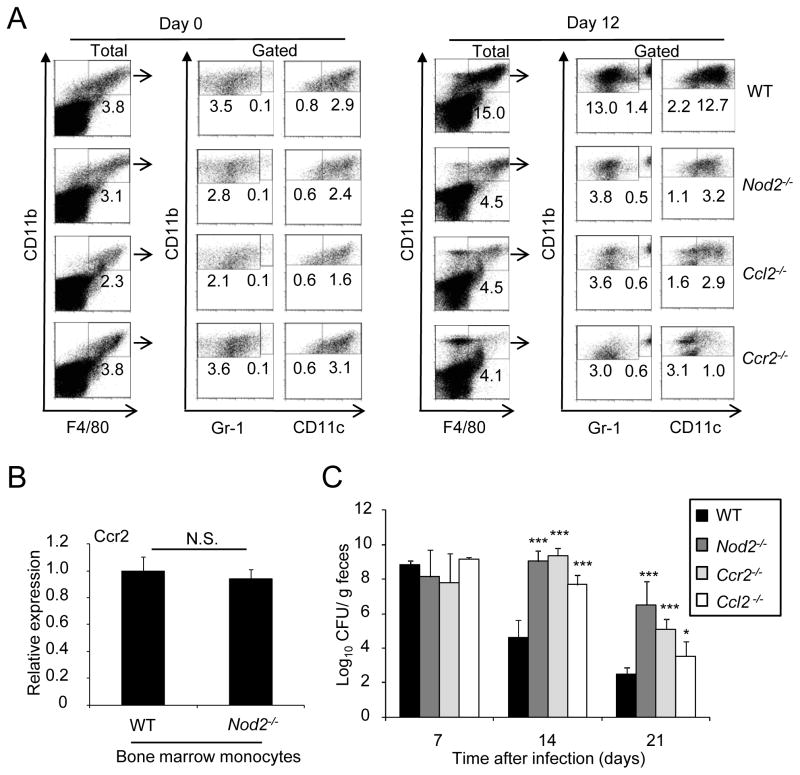
Figure 4. CCL2 and CCR2 regulate the colonic recruitment of CD11b+F4/80+ cells and clearance of C. rodentium.
(A) Cells were isolated from the colon of WT, Nod2−/−, Ccl2−/−, or Ccr2−/− mice on day 0, and 12 after oral infection with C. rodentium, and stained for CD11b, F4/80, and Gr-1 or CD11c mAb. CD11b+F4/80+ double-positive cells (% of total cells, left panel) were gated and percentage of CD11b+F4/80+Gr-1lo, CD11b+F4/80+Gr-1hi, CD11b+F4/80+CD11clo, and CD11b+F4/80+CD11chi cells in the gated population was determined. (B) Gene expression of Ccr2 was compared between bone marrow monocytes from WT or Nod2−/− mice by real-time RT-PCR. mRNA expression of Ccr2 was normalized to that of -actin. (C) C. rodentium numbers in stool from infected WT, Nod2−/−, Ccl2−/−, or Ccr2−/− mice (n= 10/group) at indicated time p. i. were determined by CFU assay. Data are means ± SD. * and *** denote significant differences between WT and Nod2−/−, Ccl2−/−, or Ccr2−/− mice at p<0.05 and P<0.001, respectively. Results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.