Table 1.
Catalyst Optimization for the Asymmetric Chlorination of 3-Phenyloxindole 1a.a
| entry | catalyst | solvent | yield (%)b | ee (%)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1d | - | toluene | < 20 | - |
| 2 | PA1 purified on silica gel | toluene | 99 | 51 |
| 3 | PA1 purified on silica gel | DCM | 99 | 48 |
| 4 | PA1 purified on silica gel | EtOAc | 99 | 50 |
| 5 | PA1 purified on silica gel | benzene | 99 | 60 |
| 6 | PA1 purified on silica gel | i-PrOAc | 99 | 80 |
| 7e | PA1 purified on silica gel | i-PrOAc | 99 | 90 |
| 7e,f | PA1 washed with HCI | i-PrOAc | 99 | 0 |
| 9e | Na[P1] | i-PrOAc | 99 | 6 |
| 10e | K[P1] | i-PrOAc | 99 | 0 |
| 11e | Mg[P1]2 | i-PrOAc | 99 | 37 |
| 12e | Ca[P1]2 | i-PrOAc | 99 | 91 |
| 13e | Sr[P1]2 | i-PrOAc | 99 | 86 |
| 14e | Ba[P1]2 | i-PrOAc | 99 | 9 |
| 15g | Ca[P1]2 | i-PrOAc | 99 | 94 |
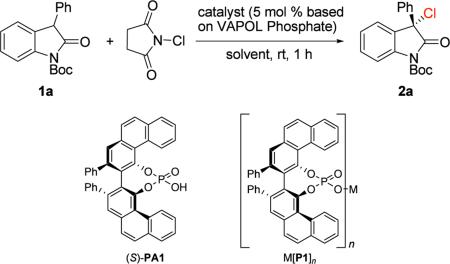
Reaction conditions: 1a (1.0 equiv), NCS (1.2 equiv), 5 mol % catalyst (based on VAPOL phosphate), with solvent indicated [0.10 M].
Isolated yield.
Enantiomeric excess determined by chiral HPLC analysis.
Reaction time of 24 h.
Reaction performed at [0.050 M].
Reaction time of 3 h.
NCS was added as a [0.12 M] solution in i-PrOAc.
