Figure 2.
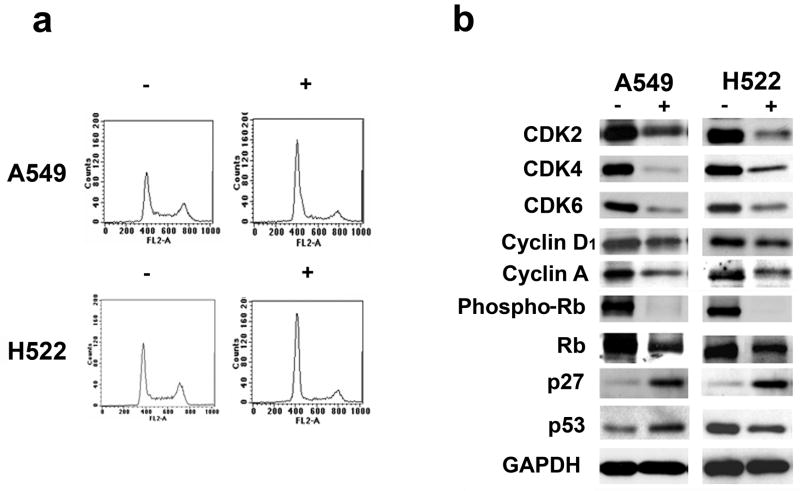
Panel a. Ritonavir causes G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in the A549 and H522 lung adenocarcinoma lines. Ritonavir was able to induce a G0/G1 block as demonstrated by increase of the G0/G1 population and by a corresponding reduction of the S and G2/M populations. Cells growth with ritonavir or vehicle are indicated with (+) and (−), respectively. For quantitation of the flow cytometry analysis see Table 2S).
Panel b. Ritonavir down-regulates the expression of numerous cell cycle-associated proteins in the lung adenocarcinoma lines A549 and H522. CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, cyclin D1, cyclin A, phospho-Rb, and Rb levels were reduced in both lines treated with ritonavir. Levels of p53 were reduced in the H522 line but increased in the A549 line. The levels of p27Kip1 were increased in both lines. For quantitation of the Western blots see Table S3.