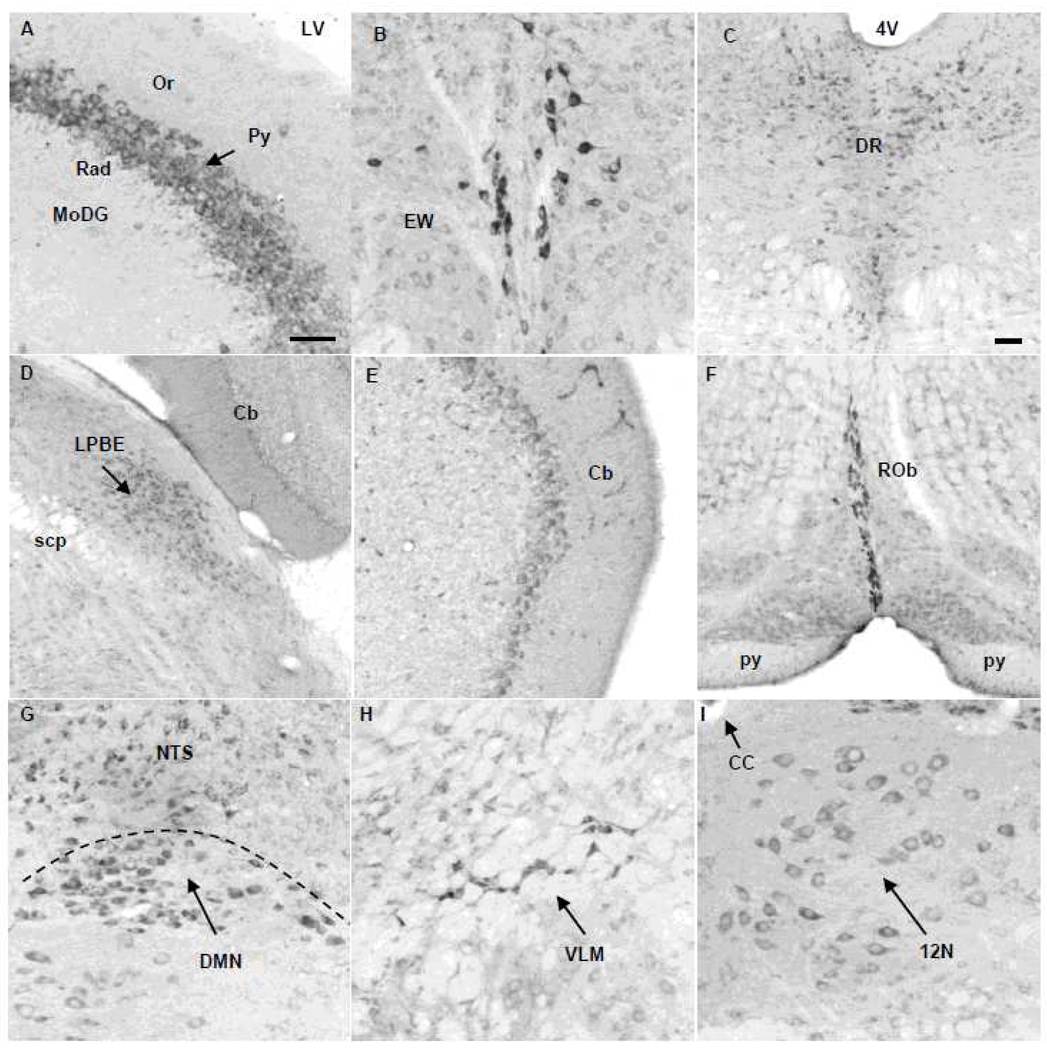
Fig. 4.
Nesfatin-1 immunoreactive cells in the hippocampus, midbrain, pons, medulla and cerebellum in naïve mice. (A) In the hippocampus, selective nesfatin-1-immunoreactive neurons are found in the pyramidal cell layer (Py). (B) Edinger-Westphal nucleus (EW). (C) Dorsal raphe nucleus (DR). (D) Lateral parabrachial nucleus, external part (LPBE). (E) Purkinje-cells in the cerebellum (Cb). (F) Raphe obscurus (ROb). (G) Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMN) and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS). (H) ventrolateral medulla (VLM, also known as A1/C1). (I) Hypoglossal nucleus (12N). Scale bar in (A) is 100 µm and representative for B, E, F, G, H, I. Scale bar in C is 100 µm and representative for (D). Other abbreviations: 4V: fourth brain ventricle; CC: central canal; LV: lateral brain ventricle; MoDG: molecular layer of the dentate gyrus; Or: oriens layer of the hippocampus; py: pyramid tract; Py: pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus; Rad: radiatum layer of the hippocampus; scp: superior cerebellar peduncle.