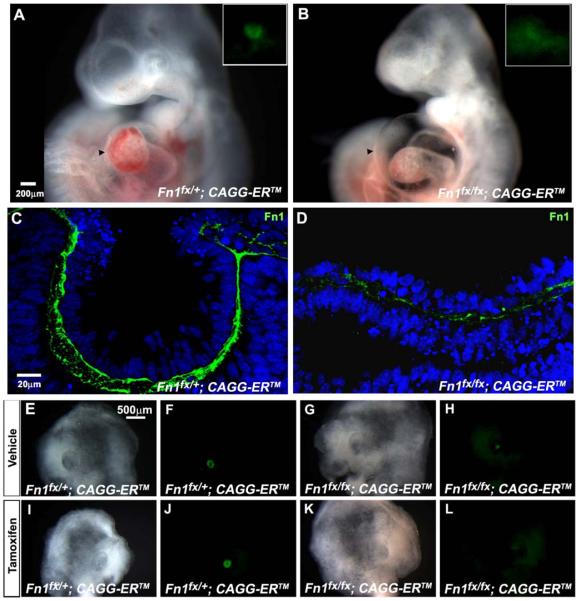
Figure 4.
Lens formation and immunostaining for fibronectin in Fn1-deficient embryos and cultured heads. (A) The lens vesicle formed in a Fn1fx/+ embryo exposed to tamoxifen on E8. GFP fluorescence, which marks the prospective lens tissue, is strong and sharply demarcated (inset). (B) No lens vesicle formed in a Fn1fx/fx embryo exposed to tamoxifen. GFP fluorescence in the ectoderm was weak and diffuse (inset) and the embryo has pericardial edema (arrowhead). (C) Fibronectin immunostaining was robust in a Fn1fx/+embryo exposed to two doses of tamoxifen on E8. (D) Fibronectin immunostaining decreased greatly and became discontinuous in Fn1fx/fx embryos exposed to two doses tamoxifen on E8. Lens formation in Fn1fx/+ and Fn1fx/fx head explants from embryos exposed to tamoxifen at E8.5 and E9.25 and cultured with or without tamoxifen from E9.5 to E11.5 (E, F, I, J). Brightfield and fluorescence images showing that lens vesicles formed in Fn+/fx; CAGG-ERTM head explants exposed to tamoxifen in E8 and cultured at E9.5 in vehicle (E, F) or in tamoxifen (I, J). (G, H) Brightfield and fluorescence images showing a small aggregate of lens cells (“lentoid”). Lentoids sometimes formed in Fnfx/fx; CAGG-ERTM head explants that received no supplemental tamoxifen during culture. (K, L) Brightfield and fluorescence images showing that lens vesicles were absent from cultured heads of Fnfx/fx; CAGG-ERTM embryos when tamoxifen was added to the culture medium.