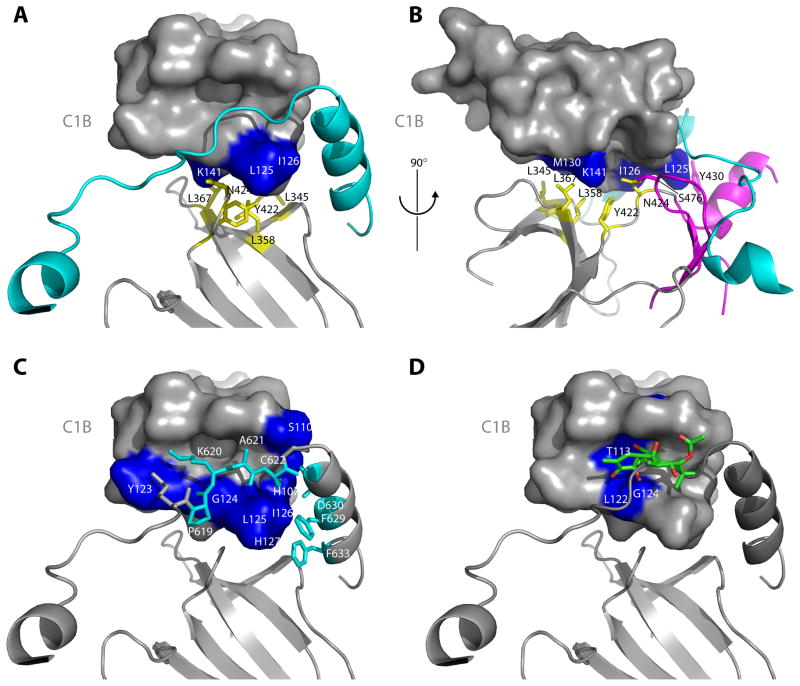
Figure 3. The C1B clamp.
(A–B) The interface between the C1B domain and the N-lobe of the catalytic domain stabilizes the clamp by positioning the C1B appropriately with respect to the NFD helix. This interface is predominantly hydrophobic, with the N-lobe side chains of Leu345, Leu358, Leu367 and Y422 (yellow, stick model) packing against Leu125, Ile126 and K141 (blue, surface model) of the C1B domain. Y430 is contributed by the C-lobe of the kinase domain (magenta). (C) The C1B domain clamps the NFD helix and residues immediately N-terminal to the helix. Residues Pro619 – Cys622 (cyan, stick model) are in an extended conformation that makes intimate contacts with the phorbol ester binding cleft of the C1B domain. (D) Comparison of the C1B domain of PKCδ bound to PMA (Zhang et al., 1995) with that of PKCβII shows a steric clash between phorbol ester and residues 619–622 running through the cleft.