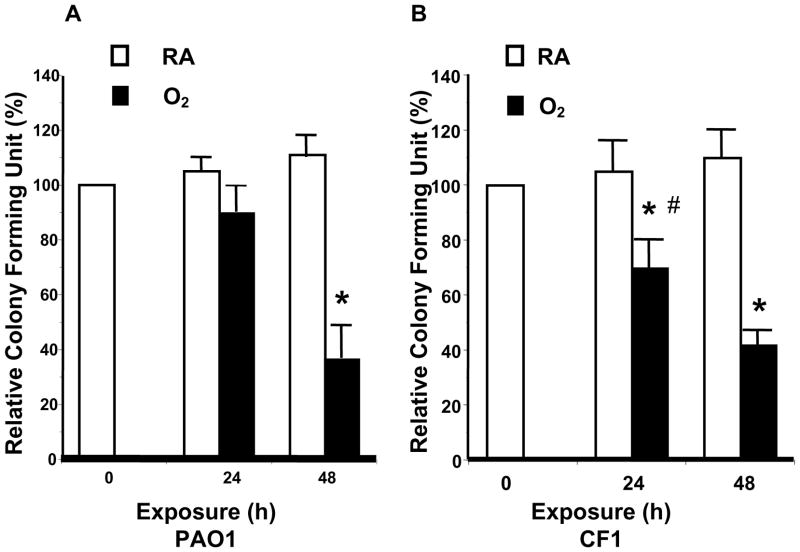
Fig. 2. Hyperoxia Reduced Viable P. aeruginosa in Macrophages.
RAW 264.7 cells were exposed to 95% O2 or to room air (RA) for indicated time periods, and then incubated for 1 h with either (A) PAO1, a non-mucoid strain of P. aeruginosa expressing green fluorescent protein, or (B) CF1, a FITC-labeled mucoid clinical isolate of P. aeruginosa. The number of viable phagocytosed P. aeruginosa was determined by colony forming unit (CFU) analysis in macrophage cell lysates. The numbers of CFU were normalized to the macrophage number and expressed as the percentage of the number obtained prior to the exposures (which was designated as 100%). *, p<0.05, compared to the room air control; #, p<0.05 compared to 24 h exposure to 95% O2 and PAO1 RCFU.