Figure 1. ROMK splice variants in the mouse kidney.
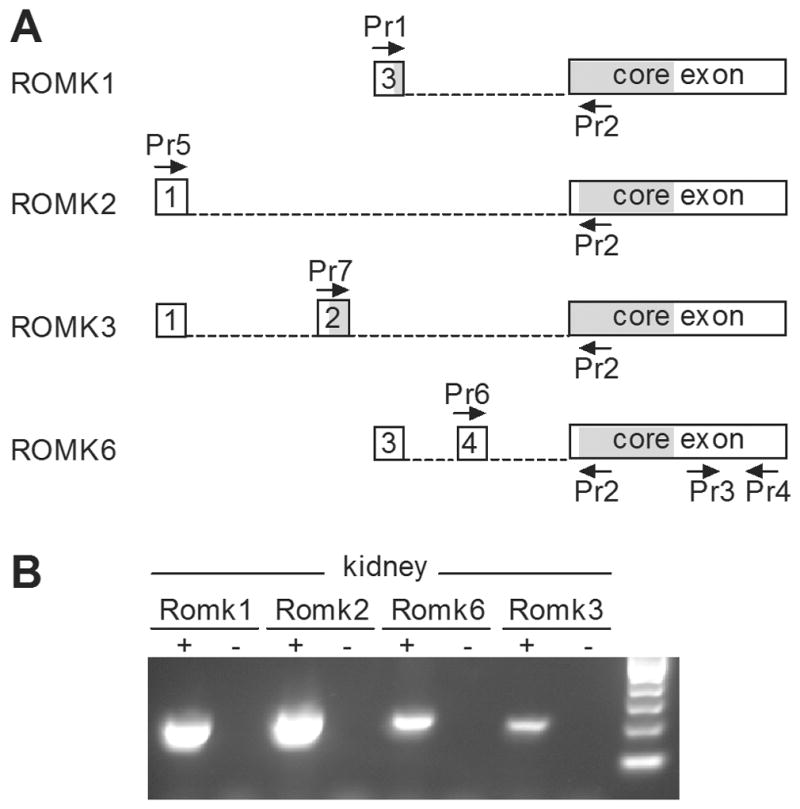
A. Schematic diagram of four predicted ROMK splice variants in the mouse, with the position of RT-PCR primers indicated by arrows. Boxes represent exons 1, 2, 3 and 4 and a common core exon included in each of the four alternatively spliced forms. Shaded segments of exons are open reading frames. Dashed lines represent introns that are spliced out. In ROMK6, several in-frame stop codons in exon 4 result in translation from a start codon in the core exon. Thus, the proteins derived from ROMK2 and ROMK6 are identical. B. RT-PCR for ROMK in adult mouse kidney. Individual splice variants were identified through a combination of specific primers and predicted length of product (as shown in A.): Romk1 (primers 1/2; 177bp), Romk2 (primers 5/2; 205bp), Romk3 (primers 7/2; 187bp), Romk6 (primers 6/2; 202bp). Each of these PCR products was sequenced to validate specificity. The negative controls (−) in each case are PCRs lacking cDNA template.
