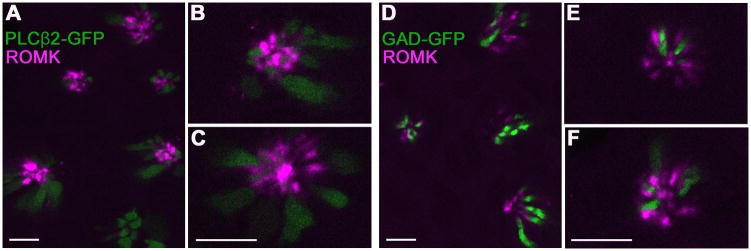
Figure 5. In cross-sections of vallate papillae, ROMK-immunoreactive cells are seen to interdigitate between Type II and Type III cells.
Confocal micrographs of cross-sectioned vallate papilla from PLCβ2-GFP mice (A–C) or GAD-GFP mice (D–F). ROMK immunoreactivity (magenta) is only near the apical tips of taste buds. At higher magnification (B, C, E, F), in this orientation also, ROMK is seen to be located in cells that are not GFP labeled in each strain (i.e. not Type II or Type III). Instead, ROMK-positive cells are adjacent to GFP-positive cells (green). For all these images, ROMK-immunostaining was visualized by tyramide signal amplification using Alexa 594-conjugated tyramide. Scale bars, 10 μm.