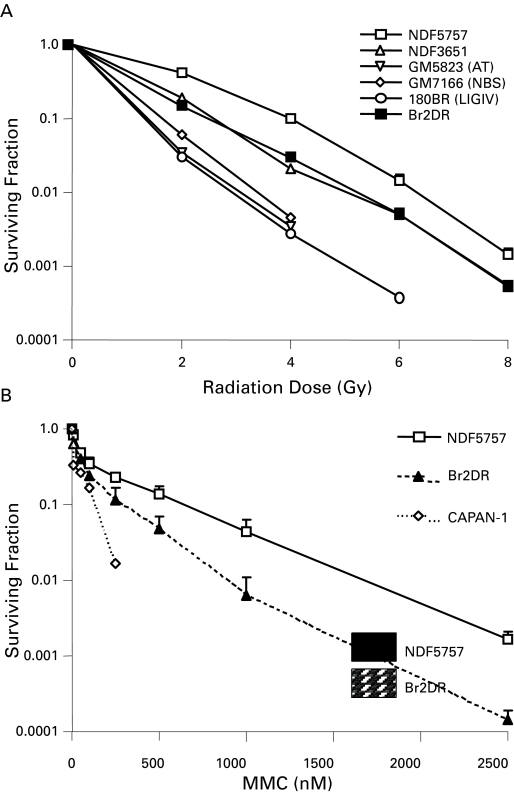
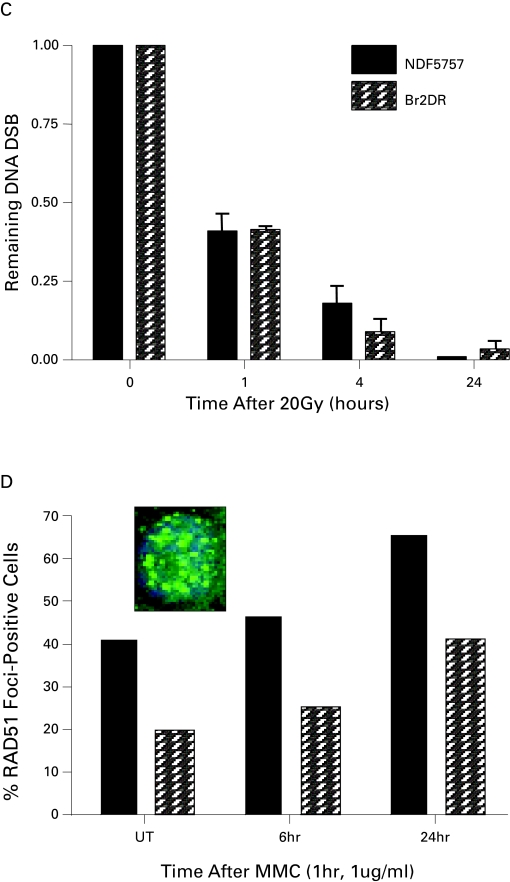
Fig. 2.
DNA Repair Assays of Heterozygote Fibroblasts Derived from Patient 2 With A BRCA2 Mutation (a,b) Shown are clonogenic survival of fibroblasts derived from patient 2 (Br2DR strain) relative to normal fibroblasts or fibroblasts defective in DNA damage sensing or repair. In (a), Br2DR cells are similar in sensitivity following ionizing radiation relative to unaffected normal fibroblast strains (NDF5757 and 3651 strains). Note exquisite sensitivity in cell strains derived from DNA damage sensing- or repair-deficient cells derived from patients with abnormal ATM, NBS1 and DNA ligase IV proteins. In (b), Br2DR cells show increased sensitivity to Mitomycin C (MMC) (p < 0.05 for each dose point) relative to a normal NDF5757 strain. Also shown in (b) is the BRCA2-deficient CAPAN-1 cell line for comparison showing exquisite MMC sensitivity. (c) Results from the neutral Comet assay measuring residual DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) as a function of time (0–24 hours) following a dose of 20 Gy. Br2DR cells show a non-significant trend towards increased residual DSBs at 24 hours. (d) Data from a RAD51 protein nuclear foci assay in which the ability for cells to increase the nuclear fraction of RAD51 foci (required for homologous recombination pathway of DSb repair) at sites of DNA damage is measured using fluorescent microscopy. An example of the foci scored in this technique is shown in the inset. The data are presented at the percent of cells positive for RAD51 foci before and after treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent, mitomycin C (MMC). A decreased RAD51 response in the Br2DR cells is observed compared to normal fibroblasts suggesting a decreased ability to mobilize RAD51 to the nucleus. Note: cells completely deficient in BRCA1 and BRCA2 function have no ability to up-regulate RAD51 foci at all.