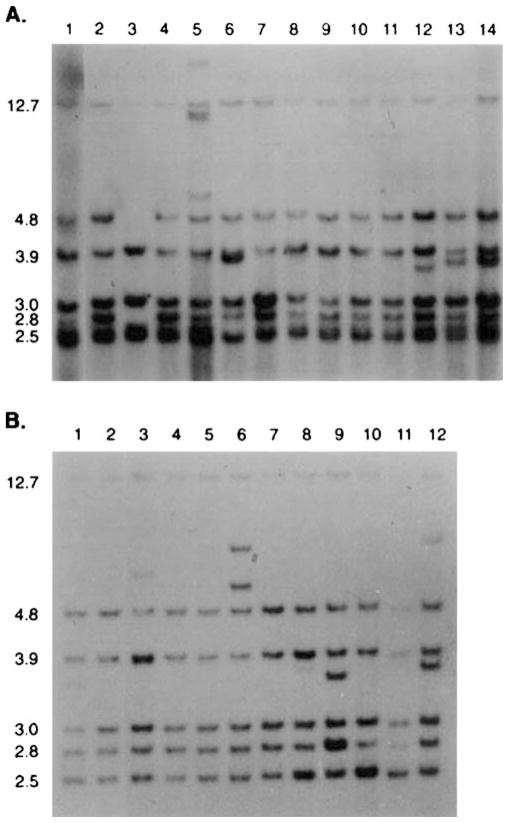
Figure 5.
(A) MMTV proviral restriction patterns are shown for DNA isolated from a premalignant hyperplastic mammary outgrowth (lanes 1 and 2) and from 12 independent mammary tumors (lanes 3–14) that arose focally within the hyperplastic population at various passages during its propagation in gland-free fat pads. The proviral content of the two different passages of the hyperplasia (lane 1 and 2) are present in all of the tumors. New MMTV proviral insertions were detected in the tumors shown in lanes 5, 12, 13 and 14. A loss of one of the original insertions was noted in the tumor DNA shown in lane 3. The DNA was digested with EcoR1 and probed with the MMTV-LTR sequence. EcoR1 cuts within the provirus and the LTR is represented at both ends of the provirus. Therefore each insertion produces two virus-host junction fragments detected by the LTR probe. In (B) the restriction enzymatic digestion and the probe were the same, however, DNA from a metastatic tumor (lane 1 in (B)) arising in the hyperplasia shown above in lanes 1 and 2, gave 11 independent lung metastases in the same mouse (shown in lanes 2–12). The tumor and all the metastases bear the original proviral insertions from the hyperplasia. Additional MMTV insertions were detected in the metastatic nodule DNA shown in lanes 6, 8, 9, 10 and 12. This strongly suggests that each metastatic lesion is an individual clone.