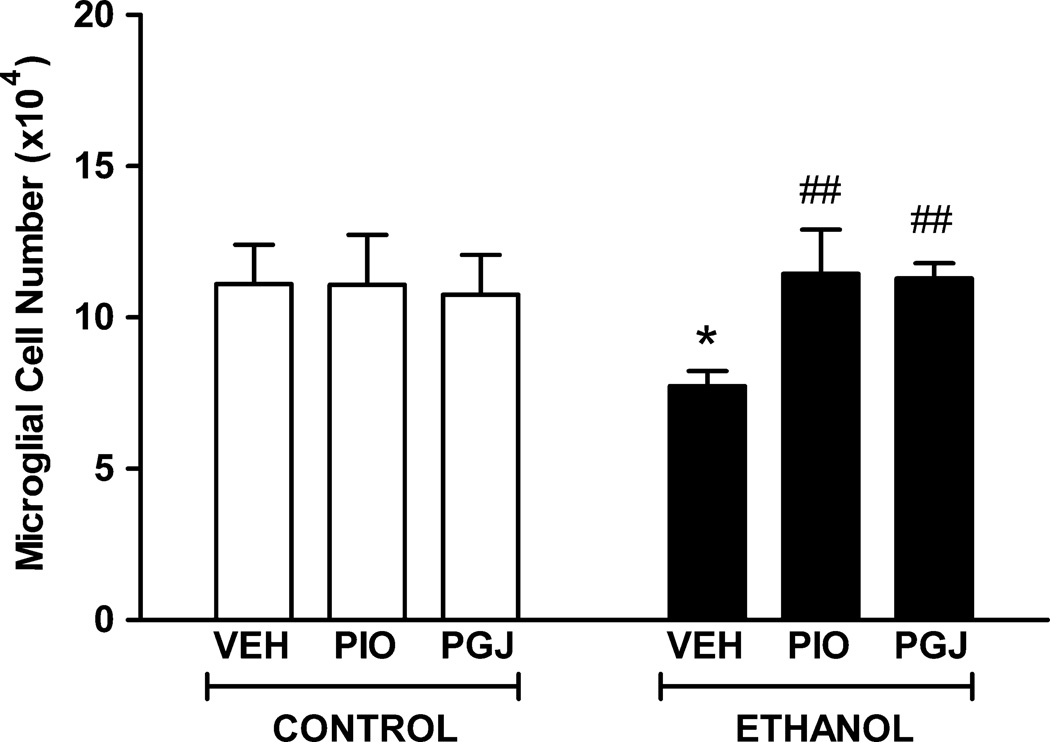
Figure 5. Protection of microglial cells in the postnatal mouse cerebellum in vivo.
Mouse pups were administered PIO or PGJ on postnatal days 2–5. Animals were given ethanol at 3.5 g/kg on postnatal days 3–5 and sacrificed on postnatal day 6. Control animals were administered vehicle (VEH) in lieu of agonist or ethanol (E). Sagittal tissue sections were stained with isolectin B4 and the number of microglial cells in the cerebellar vermis was quantified using stereological methods. Results shown are the mean ± SE of six animals in each treatment group. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA and the Fisher PLSD post hoc test. [F (5,30) = 3.261, p = 0.0181]. (* p<0.01 compared to each of the three control conditions; ## p<0.005 compared to the VEH + ethanol condition).