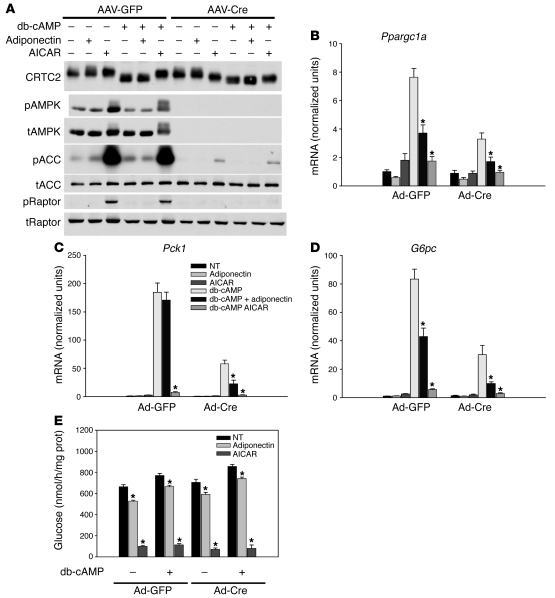
Figure 6. Adiponectin signaling in AMPK α1/α2–deficient primary hepatocytes.
(A) Western blots from hepatocytes isolated from AAV-TBG-GFP– or AAV-TBG-Cre–infected Ampkα1lox/lox;Ampkα2lox/lox mice were treated with 30 μg/ml adiponectin, 500 μM AICAR, and 100 μM db-cAMP for 6 hours and probed for CRTC2, total and phosphorylated AMPK, total and phosphorylated ACC, and total and phosphorylated Raptor. (B–D) Primary hepatocytes isolated from AAV-TBG-GFP– or AAV-TBG-Cre–infected Ampkα1lox/lox;Ampkα2lox/lox mice were treated with 30 μg/ml adiponectin, 500 μM AICAR, and 100 μM db-cAMP for 6 hours. Total RNA was isolated and (B) Ppargc1a, (C) Pck1, and (D) G6pc mRNA was quantified and expressed relative to cyclophilin A mRNA and normalized to basal mRNA from GFP-infected hepatocytes. *P < 0.05 versus db-cAMP. (E) Primary hepatocytes isolated from AAV-TBG-GFP– or AAV-TBG-Cre–infected Ampkα1lox/lox;Ampkα2lox/lox mice were treated with 30 μg/ml adiponectin, 500 μM AICAR, and 100 μM db-cAMP for 6 hours in glucose-free medium. Glucose production was measured and normalized to total protein. *P < 0.05 versus untreated with adiponectin or AICAR. All results are expressed as the mean, and error bars represent SEM.