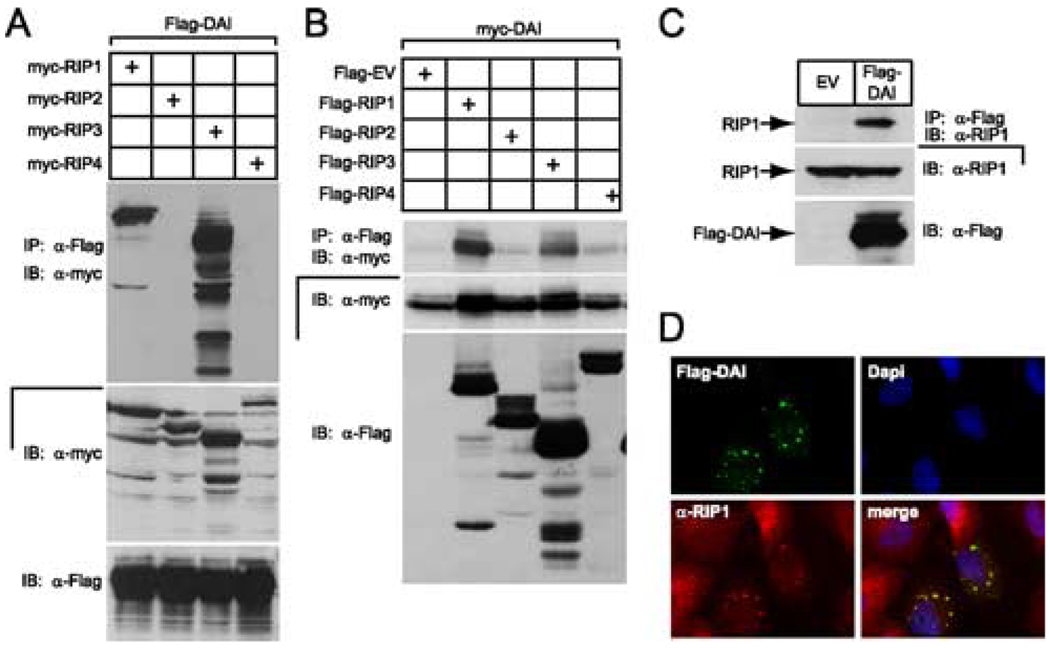
FIGURE 2.
DAI interaction with the RHIM-containing RIP kinases, RIP1 and RIP3. A, Autoradiogram of IB and IP of 293T cell extracts following transfection of myc epitope-tagged RIP1, RIP2, RIP3, or RIP4 together with Flag epitope-tagged DAI vectors. B, Autoradiogram of IB and IP of 293T cell extracts following transfection of Flag epitope-tagged RIP1, RIP2, RIP3, and RIP4, or an EV together with myc epitope-tagged DAI vector. Cellular lysates were subjected to anti-Flag IP and analyzed by IB with anti-myc Ab. IB analysis of total cell lysate showed the relative expression of Flag and myc epitope-tagged proteins. C, Demonstration that Flag-DAI binds endogenous RIP1 via IB of 293T cells following transfection with Flag epitope-tagged DAI or an EV. IP was with anti-FLAG M2 beads and IB was with anti-RIP1 Ab. Total cell lysates were examined for the expression of RIP1 and Flag-DAI. D, Immunofluorescent localization of Flag-DAI with endogenous RIP1. HeLa cells were transfected with Flag-tagged DAI and then stained with rabbit anti-Flag Ab and with monoclonal anti-RIP1 Ab for endogenous RIP1. Flag-DAI was detected by an anti-rabbit Alexa-488-conjugated secondary Ab and RIP1 was detected by an anti-mouse Alexa-594-conjugated secondary Ab. Stained cells were examined by epifluorescent microscopy (×1000).