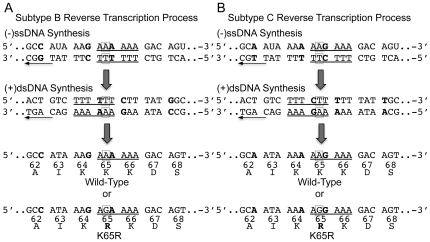
Figure 1. Sequence comparison of the RT region of the pol gene derived from subtype B and C HIV-1 spanning codons 62 to 68.
(A) Outline of the reverse-transcription process in subtype B HIV-1 leading to either wild-type or K65R-containing transcripts. The K65R mutation results from an AAA-to-AGA mutation in subtype B HIV-1. (B) Outline of the reverse-transcription process in subtype C HIV-1 leading to either wild-type or K65R-containing transcripts. The K65R mutation results from an AAG-to-AGG mutation in subtype C HIV-1. The genomic sequences of the subtype B and C RT segments of pol spanning codons 62 to 68 are indicated. (−)ssDNA synthesis from the viral (+)ssRNA genome and (+)dsDNA synthesis from the (−)ssDNA intermediate are also depicted. Underlined are the homopolymeric nt stretches of both templates at their specific locations. In bold are the nt polymorphisms that exist between both subtypes in this region. Highlighted in a square is the base that, once mutated, gives rise to the K65R drug resistance mutation.