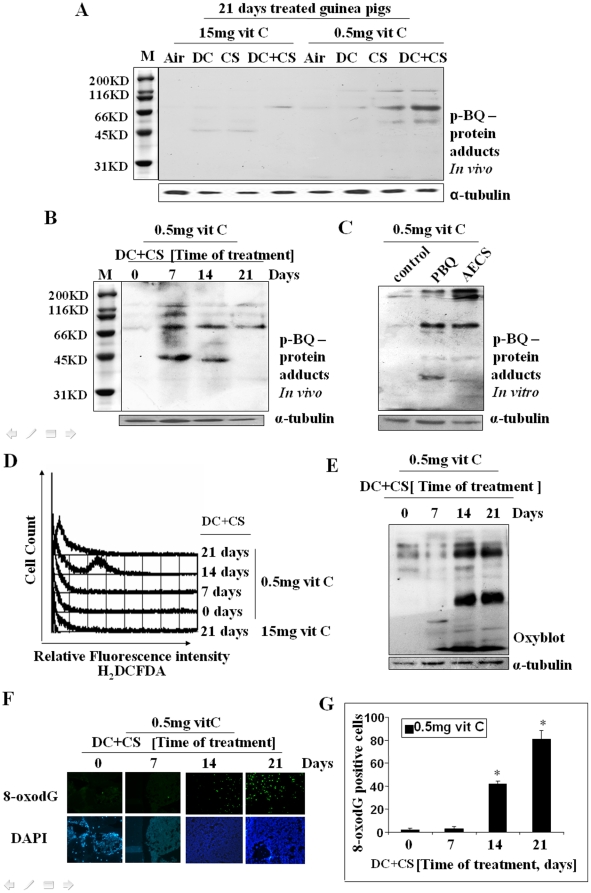
Figure 4. Identification of p-BQ-protein adducts and detection of oxidative stress in bone marrow cells of guinea pigs.
(Panel A) p-BQ protein adducts in the bone marrow cells of CS-exposed guinea pigs on day 21 in vivo. (Panel B) p-BQ protein adducts in CS-exposed guinea pigs at different time period in vivo. (Panel C) p-BQ protein adducts formed in marrow cells in vitro after incubation with p-BQ and AECS (aqueous extract of cigarette smoke), respectively; M, marker (cropped). (Panel D) ROS production in MDS guinea pigs at different time periods, as evidenced by flow cytometry. The X-axis represents the intensity of dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA). (Panel E) Protein oxidation as evidenced by oxyblot indicating formation of protein carbonyl. (Panel F) DNA oxidation as evidenced by the formation of 8-oxodG; upper row: green fluorescence indicates formation of 8-oxodG; lower row: stained with DAPI; (magnification 200×). (Panel G) Quantitative evaluation of 8-oxodG; * indicates significant difference from 0 and 7 days. Vit C means vitamin C.