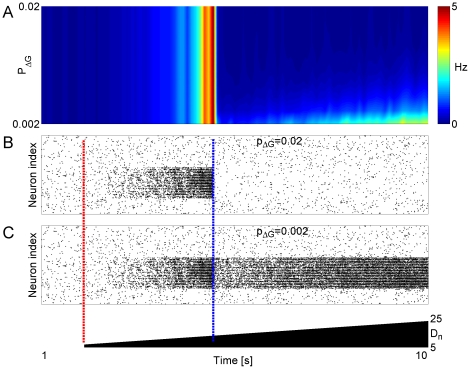
Figure 6. Changes in network topology and membrane conductance underlie the overall effect of gap junction connectivity on the network stability.
A Color panel is the surface plot of firing rate (averaged
over non-overlapping bins of 100 ms and over all model neurons) vs. the
probability 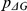 to
increase the leak conductance by
to
increase the leak conductance by 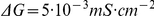 in each
one of the model neurons from the affected area
(
in each
one of the model neurons from the affected area
(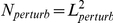 ,
,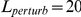 ) that did
not previously share gap junction connection. Color code is blue for low
firing rate and red for high firing rate. Horizontal axis is simulation
time ([0–10] seconds). Background noise intensity
) that did
not previously share gap junction connection. Color code is blue for low
firing rate and red for high firing rate. Horizontal axis is simulation
time ([0–10] seconds). Background noise intensity
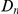 for the
set of
for the
set of 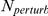 model
neurons was perturbed at
model
neurons was perturbed at 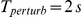 (dashed
red line through Panels B,C), and progressively increased to achieve
5-fold higher values at time 10 seconds (scale bar in lowest panel).
Membrane leak conductance for
(dashed
red line through Panels B,C), and progressively increased to achieve
5-fold higher values at time 10 seconds (scale bar in lowest panel).
Membrane leak conductance for 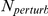 model
neurons was increased (as specified by
model
neurons was increased (as specified by 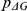 ) at time
) at time
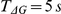 (dashed
blue line through Panels B,C). B Raster plot of
network's activity for
(dashed
blue line through Panels B,C). B Raster plot of
network's activity for 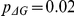 . Other
parameters:
. Other
parameters: 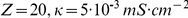 .
C Third panel: Raster plot of network's activity
for
.
C Third panel: Raster plot of network's activity
for 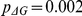 . Other parameters:
. Other parameters:
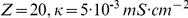 .
.