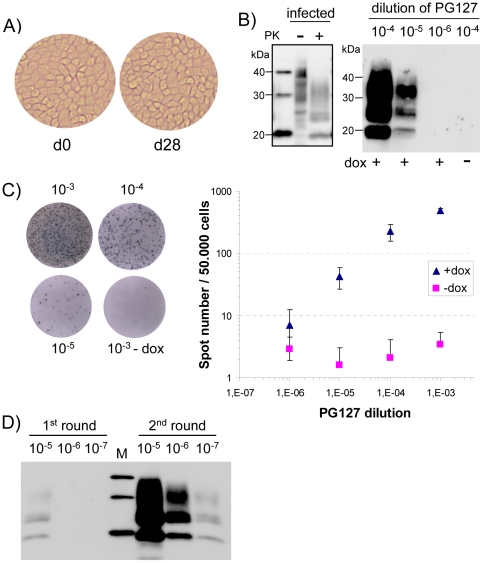
Figure 1. Sensitivity of ovRK13 cell assay for the detection of PG127 ovine prion.
A) Morphology of inoculated ovRK13 cultures kept in the same wells during the whole cell assay procedure (d0 is the time of inoculation and d28 is 4 weeks later). B) Sensitivity of ovRK13 cell assay as assessed by immunoblotting. Right panel: Serial 10-fold dilutions (from 10−4 to 10−6) of infectious PG127 10% brain homogenate were inoculated to single wells of ovRK13 cells. Four weeks later, inoculated cultures were analyzed for PrPres by immunoblotting. Positive transmission was detected for dilutions up to 10−5. No PrPres was observed when inoculated ovRK13 did not express the ovine PrP (dox-). Left panel: total PrP from infected cells was analyzed before (−) or after (+) PK digestion to illustrate band shift upon PK proteolysis. M are standard molecular mass marker proteins (20, 30 and 40 kDa). C) Sensitivity of ovRK13 cell assay as assessed by Elispot. Replicate wells from the same experiment shown in Fig. 1B were analyzed. Left: representative wells of an Elispot plate showing spots given by ovRK13 cells exposed to the indicated dilutions of PG127. Right: double-logarithmic plot of spot number versus PG127 dilution shown for inoculations in the presence (triangle) or in the absence (square) of dox. For each dilution, the mean value ± SD of 8 measurements is shown. Background values for ovRK13 cells inoculated in the absence of dox are less than 4 spots per 50,000 cells. D) Sensitivity is strongly improved by 2 successive rounds of cell assay. Serial 10-fold dilutions (from 10−5 to 10−7) of infectious PG127 10% brain homogenate were inoculated to duplicate wells of ovRK13 cells. Four weeks later, PrPres in a 1st set of inoculated cultures was isolated (1st round) while cultures of the 2nd set were homogenized to inoculate new ovRK13 cells. Four weeks later, PrPres was isolated (2nd round) and all the samples were analyzed by immunoblotting. M are standard molecular mass marker proteins (20, 30 and 40 kDa).