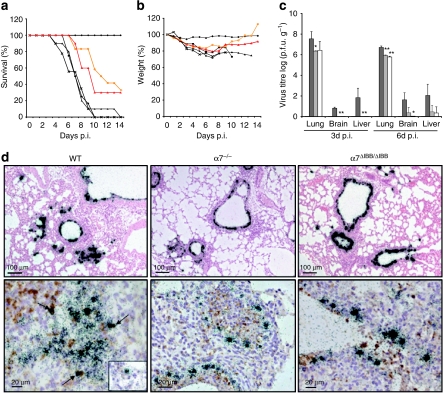
Figure 2. Pathogenicity of SC35M in WT and importin-α-knockout animals.
WT (black square; n=18), α4−/− (black triangle; n=16), α5−/− (black cross; n=16), α7−/− (red triangle; n=16) and α7ΔIBB/ΔIBB (orange circle; n=18) animals were infected with 100-fold LD50 of SC35M. Control groups received PBS (black diamond). (a) Survival and (b) weight loss were monitored for 14 days. (c) Virus titres in the lung, brain and liver homogenates of controls (black columns) and infected WT (dark grey columns), α7−/− (light grey columns) and α7ΔIBB/ΔIBB (white columns) animals were determined by plaque assays. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of viral titres detected in three animals per time point. The detection limit was ≥30 p.f.u. (d) In situ hybridization (upper panels) shows severe infection of epithelial cells with classical signs of primary viral pneumonia with extensive infiltration and destruction of the alveolae in WT mice (upper left panel) in contrast to mostly intact lung tissues of α7−/− or α7ΔIBB/ΔIBB animals (upper middle and right panel). Double-labelling experiments (lower panels) demonstrate virus RNA-positive Mac-3+ macrophages in the lungs of WT mice (lower left panel, arrows and inset) but not in α7−/− or α7ΔIBB/ΔIBB animals infected for 3 days (lower middle and right panel), respectively. The statistical significance of differences in lung titres of WT and importin-knockout animals were assessed by Student's t-test (*P<0.05; **P<0.01).