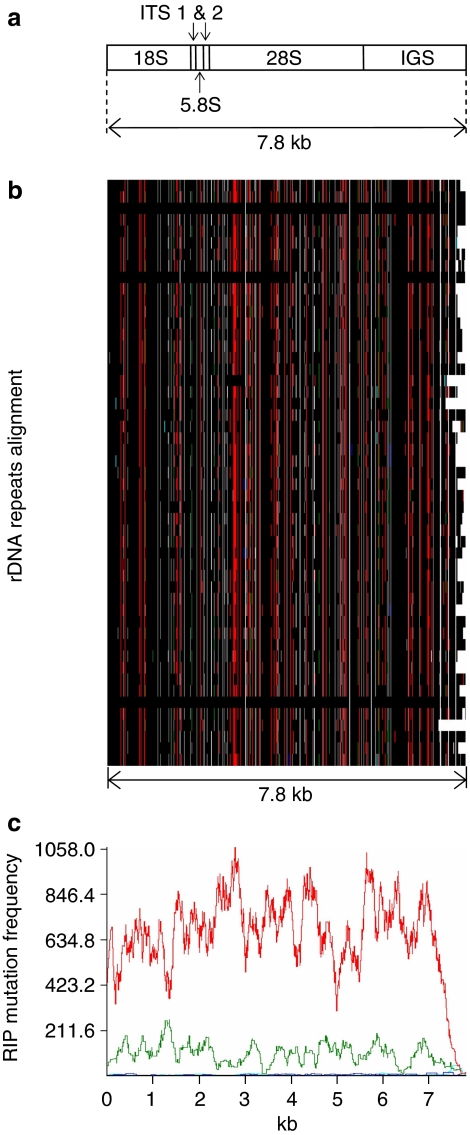
Figure 3. Repeat-induced point (RIP) mutation in ribosomal DNA of L. maculans shown as RIPCAL output.
(a) Schematic representation of the rDNA unit in L. maculans (ITS, internal transcribed spacers; IGS, intergenic spacer); (b) a schematic multiple alignment of the 7.8 kb 'complete' ribosomal DNA (rDNA) units occurring in SuperContigs 2 and 19. Polymorphic nucleotides are coloured as a function of the type of RIP mutation observed, with black, invariant nucleotide; red, CpA  TpA or TpG
TpA or TpG  TpA mutations; dark blue, CpC
TpA mutations; dark blue, CpC  TpC or GpG
TpC or GpG  GpA mutations; pale blue, CpT
GpA mutations; pale blue, CpT  TpT or ApG
TpT or ApG  ApA mutations; green, CpG
ApA mutations; green, CpG  TpG or CpG
TpG or CpG  CpA mutations; (c) RIP mutation frequency plot over a rolling sequence window, corresponding to the multiple alignment directly above. Nucleotide polymorphisms (against the alignment consensus, which is also the highest GC-content sequence) mostly correspond to CpA
CpA mutations; (c) RIP mutation frequency plot over a rolling sequence window, corresponding to the multiple alignment directly above. Nucleotide polymorphisms (against the alignment consensus, which is also the highest GC-content sequence) mostly correspond to CpA  TpA or TpG
TpA or TpG  TpA (red curve) and CpG
TpA (red curve) and CpG  TpG or CpG
TpG or CpG  CpA (green curve).
CpA (green curve).