Figure 4.
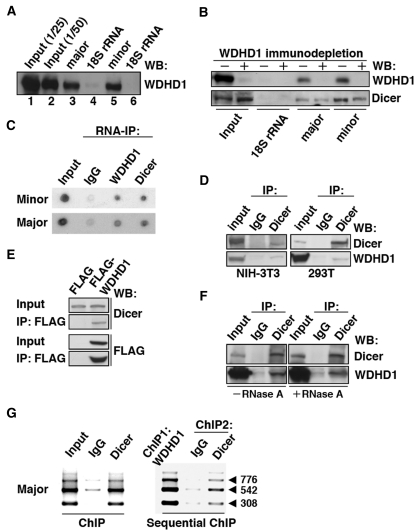
WDHD1 associates with the centromere-encoded RNA transcripts. (A and B) RNA pull-down assay was carried out using biotinylated RNA transcripts. (A) In vitro transcribed RNAs corresponding to approximately one repeat of the centromeric major (lane 3) and minor (lane 5) satellite sequences were used as the baits. Precipitated proteins were visualized by western blotting using anti-WDHD1 antibody. Input represents direct loading that equals to 1/25 or 1/50 of the lysate protein used in the pull-down (lanes 1 and 2). Transcripts corresponding to 300 nt (lane 4) and 162 nt (lane 6) of the 18S rRNA sequence serve as controls for the major (lane 3) and minor (lane 5) satellite transcripts, respectively. (B) Dicer association with centromeric RNA sequences attenuated upon WDHD1 depletion. Cell lysates were subjected to immunodepletion using control IgG or WDHD1-specific antibodies, followed by RNA pull-down assay as in (A). (C) RNA-immunoprecipitation assay was performed using antibodies against the indicated proteins (WDHD1 and Dicer). RNA was extracted from the immunoprecipitates and subjected to dot blot analysis using probes corresponding to the sequences of the minor (upper) or major (lower) satellite repeats. (D–F) Association of WDHD1 with Dicer. (D) Anti-Dicer immunoprecipitates (IP) using extracts (input) prepared from NIH-3T3 (left) or 293T (right) cells were probed with antibodies against WDHD1 (top) and Dicer (bottom). (E) 293T cells were transfected with constructs encoding FLAG or FLAG-tagged WDHD1. Immunoprecipitation (IP) of the cell lysates was done using FLAG antibodies, and subsequently analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against FLAG (top) and Dicer (bottom). Extent of overexpression and subcellular localization of the FLAG-WDHD1 protein are shown in the Supplementary Information (Supplementary Figure S3). (F) 293T cell lysates were treated with (+) or without (−) RNase A prior to anti-Dicer immunoprecipiation as above. (G) Dicer occupancy of centromeric repeat regions. ChIP assays were performed on crosslinked chromatin from NIH-3T3 cells using antibodies specific for Dicer or control rabbit antibodies (IgG) (left panel). Sequential ChIP analysis was done to assess co-occupancy of the centromere by both WDHD1 and Dicer (right panel). Products of final PCR analysis using primers specific to major satellite repeat DNA sequence are resolved in agarose gel.