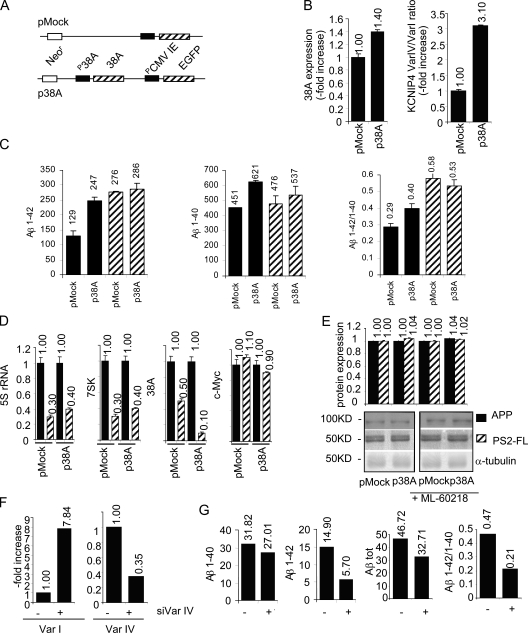
Figure 5.
38A-induced perturbation of Aβ secretion. (A) A schematic view of p38A and pMock plasmid constructs used to generate p38A-SHSY5Y and pMock-SHSY5Y permanently transfected cell lines. (B) Real-time RT-PCR quantitative determination of 38A expression and KCNIP4 splice variant ratio in p38A-SHSY5Y and pMock-SHSY5Y permanently transfected cell lines. (C) Increased β-amyloid secretion and perturbation of the Aβ x-42/Aβ x-40 ratio in 38A-overexpressing SHSY5Y cells. X axis, transfected plasmids; y axis, quantitative determination of Aβ (picograms/milliliter) secreted in the medium 48 h after medium replacement as determined by sandwich ELISA. The resulting Aβ x-42/Aβ x-40 ratio is reported. Striped bars, samples treated with ML-60218 PolIII-specific inhibitor; shaded bars, untreated cell samples. (D) A demonstration that PolIII transcription is specifically inhibited in ML-60218-treated cells, whereas it does not affect PolII activity. 5S rRNA, 7SK RNA, 38A, and c-Myc transcript abundancies were detected by real-time RT-PCR in cells treated with ML-60218 and in untreated controls used as described in A. (E) Quantitative Western blotting analysis of APP and PS2 synthesis in pMock- and/or p38A-transfected cells in ML-60218–treated and –untreated conditions. All of the determinations were normalized to α-tubulin detections. (F and G) Suppression of the biological phenotype driven by the coexpression of 38A and KCNIP4 Var IV–specific silencing plasmid in SHSY5Y cells. Three independent determinations of Var IV decrease and the concomitant increase of Var I expression are shown together with the determinations of Aβ secretion in siVar IV silenced (+) with respect to cells transfected with a scrambled siRNA (−). The error bars were not relevant enough to be visible in the graphs; additional repetitions of the same experiment gave similar results (not depicted).