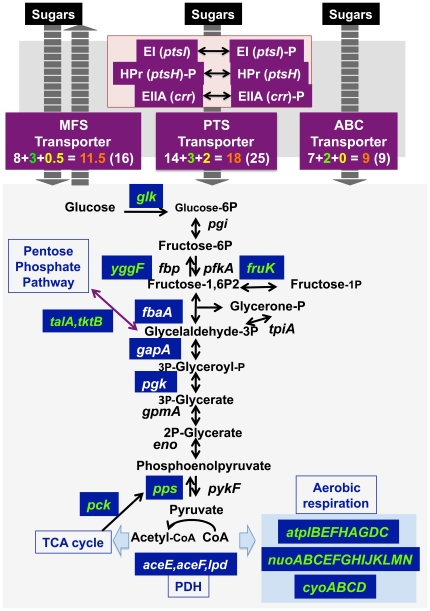
Figure 5. Regulatory roles of CRP.
Upper panel: The genes under the control of CRP are indicated under either purple background (the genes for sugar transport systems) or blue background (the genes for metabolic enzymes). CRP regulates the majority of genes for three pathways of sugar transport (MFS, PTS and ABC). The number in boxes represent in the order from left to right: The number of CRP target genes listed in Regulon DB (white); the number of genes identified to be regulated by CRP in this study (green); the number of genes predicted to be under the control of CRP in this study (yellow); the total number of genes under the control of CRP (orange). The numbers shown in parenthesis represent total number of genes constituting the respective transport systems, including those not regulated by CRP. Lower panel: Most of the genes for the enzymes involved in glycolysis are controlled by Cra [30] while only three genes, fbaA, gapA and pgk, had been identified as the regulation targets of CRP (shown in while under blue background). In this study, we identified a number of novel targets of CRP (shown in green under blue background). Furthermore a number of the genes involved in the metabolism downstream of glycolysis including PDH pathway and aerobic respiration were found to be the targets of CRP regulation. The number of target 0.5 represents such a particular case as fbaB<CRP>yegT (see Table S3), in which one (fbaB) of the divergent promoters is known under the control of CRP but possible regulation of the opposite promoter (yegT) by CRP can not be ruled out.