Fig. 3.
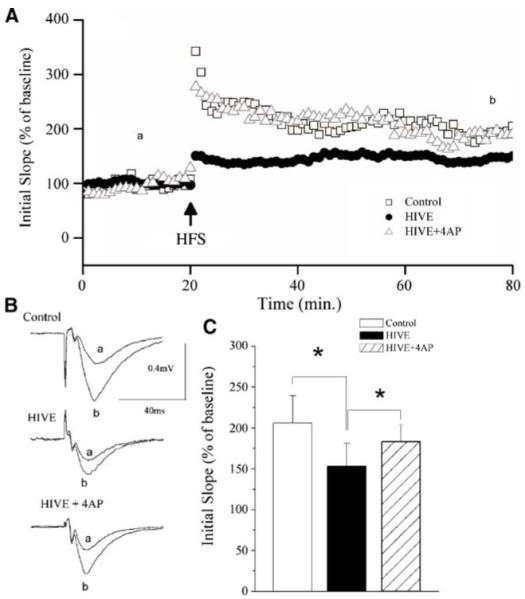
4-AP attenuates HIV-induced inhibition of LTP in the CA1 region of SCID mouse hippocampal slices. SCID mice were injected with HIV-1ADA-infected macrophages or uninfected macrophages, and a subgroup of those injected with HIV-1ADA-infected macrophages were daily administered with 4-AP (5 mg/kg). A The time course and magnitude of LTP in the Schaffer collateral to CA1 synapses recorded from hippocampal slices prepared from SCID mice injected with either HIV-1ADA-infected macrophages (HIVE), uninfected macrophages (control), or HIV-1ADA-infected macrophages and 4-AP (HIVE+4AP). The graph plots the initial slope of the evoked EPSPs recorded from the CA1 dendrite field (stratum radium) in response to constant current stimuli. HFS (500 ms×2) was delivered at the time indicated by an arrow. Each point in the graph is an average of three consecutive sweeps. Note that injection of HIV-1ADA-infected macrophages inhibited LTP (circle) and administration of 4-AP abolished the HIV-1ADA-associated inhibition (triangle). B Individual fEPSPs taken from different time points (a) before and (b) after HFS. C The bar graph showing the average LTP during the last 20 min of each group, demonstrating that HIV-1 inhibits LTP and systemic administration of a Kv channel antagonist, 4-AP, significantly blocked the HIV-1-associated inhibition
