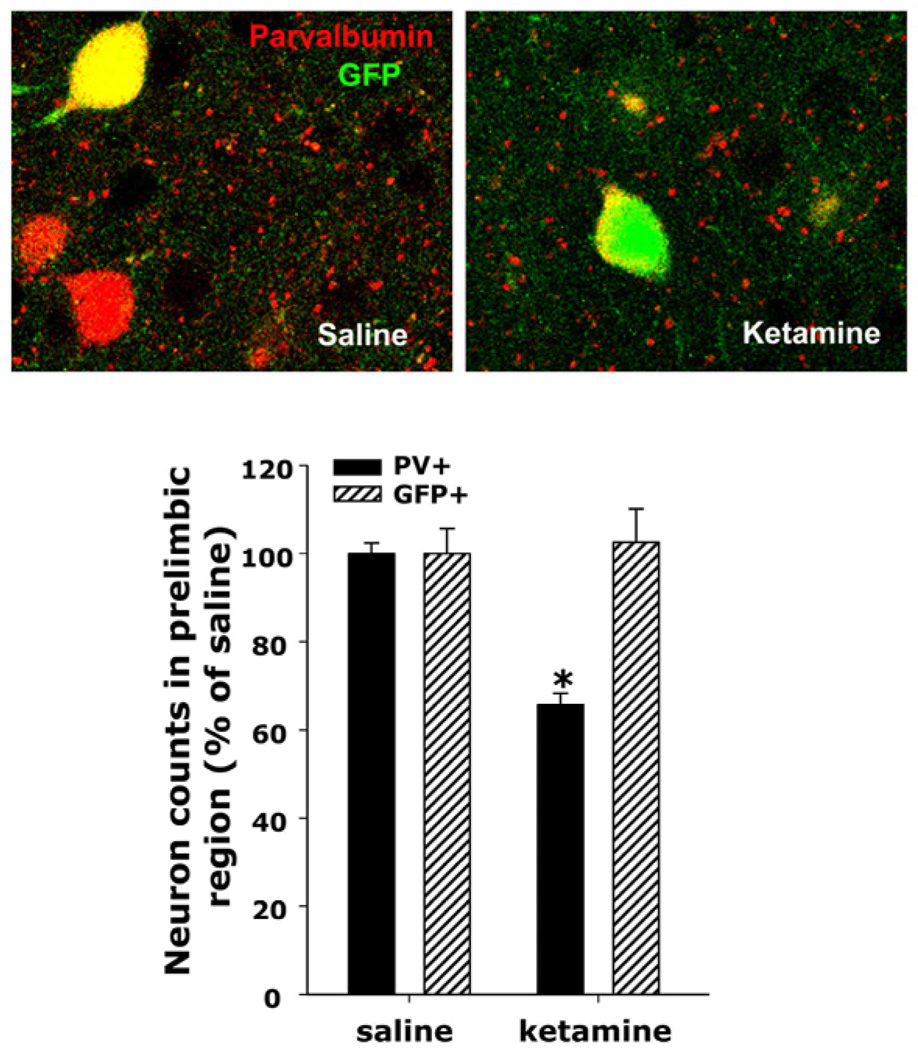
Figure 2. Loss of PV-expression without death of the interneurons.
The heterozygous progeny of G42 X C57BL/6 crossings was treated with saline or ketamine during the second postnatal week as described in figure 1 and the animals were perfused between the 5th and 6th week of age. The G42 line expresses GFP in approximately 50% of PV+ interneurons (Chattopadhyaya et al., 2004; Di Cristo et al., 2004). (A) Colocalization of GFP and PV was determined by confocal microscopy using a Zeiss Pascal system and AlexaFluor 568 as secondary antibody for detection of PV. (B) The prelimbic region on each slice was imaged across six consecutive slices, and across 16 mm on the Z axis. Images were then collapsed and the number of cells expressing PV or GFP were counted as described in figure 1 and normalized by the mean of the saline controls. As described in figure 1, there was a statistically significant decrease in the number of PV-expressing neurons, but there was no decrease in the GFP-expressing population. Since all GFP expressing neurons were also positive for PV in saline controls, as previously described (Chattopadhyaya et al., 2004; Di Cristo et al., 2004), these results suggest that the PV-interneuronal population is still present in these animals, but the neurons do not express their characteristic marker, parvalbumin.
Bar graphs represent means ± SEM. * indicates statistical significance (p < 0.005) with respect to saline as determined by ANOVA (F(3,12) = 12.278, p < 0.001) followed by Tukey’s pos hoc test.