Fig. 2.
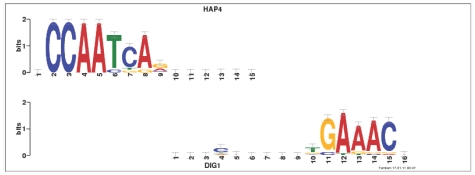
Example of uninformative alignments in ‘real data’. This alignment between the query motif DIG1 and the target motif HAP4 is one of several such spurious alignments reported by Tomtom as significant (P-value 0.00014, q-value 0.0068) when querying the MacIsaac set of yeast motifs (MacIsaac et al., 2006) against itself (using ED). All these uninformative alignments are no longer reported when the same experiment is repeated with the ‘complete-scores’ option turned on (3).