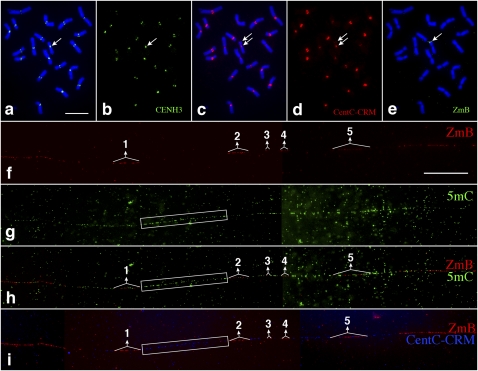
Figure 6.
Mapping of DNA methylation in an inactivated B centromere. (a) Immunofluorescence assay using a maize anti-CENH3 antibody on somatic metaphase chromosomes of maize line 9-Bic-1. The arrow points to the 9-Bic-1 chromosome containing a normal centromere from maize chromosome 9 and an inactivated centromere of the maize B chromosome. CENH3 signals, indicated by an arrow, were only observed in the functional centromere derived from chromosome 9. Bar, 10 μm. (b) Digitally separated CENH3 signals. The arrow points to the single CENH3 signal associated with the dicentric chromosome. (c) FISH of the same metaphase cell using a mixed probe containing both CentC satellite and CRM sequences. The two arrows point to the normal centromere and the inactivated B centromere, respectively. (d) Digitally separated FISH signals. CentC-CRM signals were associated with both the normal and the inactivated B centromeres (arrows). (e) FISH of the same metaphase cell using a ZmB probe. The arrow points to the distinct signal associated with the inactivated B centromere. (f) Fiber-FISH signals from the ZmB repeat in the inactivated B centromere. Bar, 25 μm. (g) Detection of 5mC on the same DNA fiber as f. (h) A merged image of the ZmB and 5mC signals. The 5mC signals were distributed throughout the DNA fiber. (i) Fiber-FISH signals derived from ZmB (red) and a mixed probe with both CentC and CRM sequences (blue). The five ZmB repeat arrays associated with the CENH3 domain are labeled. The boxes cover the centromeric region flanked by the ZmB repeat arrays #1 and #2. This region contains mainly CentC-CRM sequences and is extensively methylated.