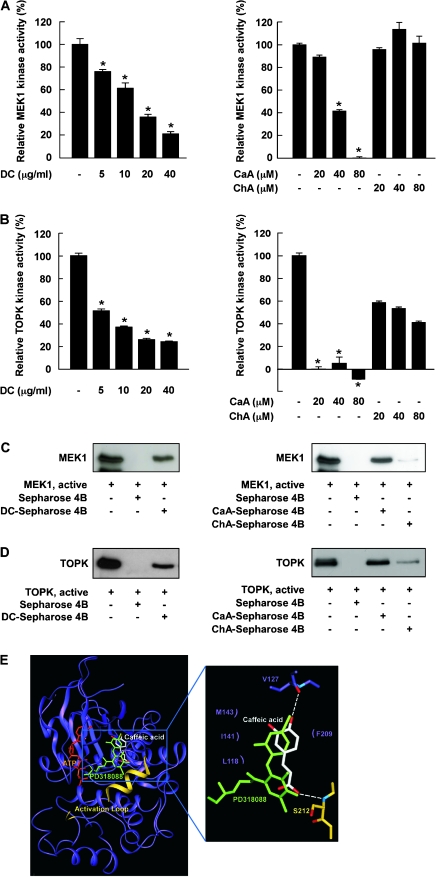
Fig. 3.
Effects of DC, CaA or ChA on MEK1 or TOPK kinase activity and direct binding with MEK1 or TOPK. (A, left) DC and (right) CaA, but not ChA, inhibit MEK1 activity. (B, left) DC and (right) CaA and ChA inhibit TOPK activity. Kinase activities are expressed as percent inhibition relative to respective untreated control. Data are presented as means ± SDs from three independent experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate a significant decrease in kinase activity in groups treated with active MEK1 or TOPK and DC, CaA or ChA and the group treated with active MEK1 or TOPK alone (P < 0.05). (C, left) DC or (right) CaA, but not ChA, binds specifically with MEK1. (D, left) DC or (right) CaA, but not ChA, binds with TOPK. Binding was confirmed by immunoblotting: lane 1 (input control), MEK1 or TOPK protein standard; lane 2 (negative control); lane 3, MEK1 or TOPK pulled down using DC-Sepharose 4B (left) or CaA-Sepharose 4B (right) affinity beads and lane 4, MEK1 or TOPK pulled down using ChA-Sepharose 4B (right) affinity beads. (E) Modeling study of the binding of CaA to MEK1.