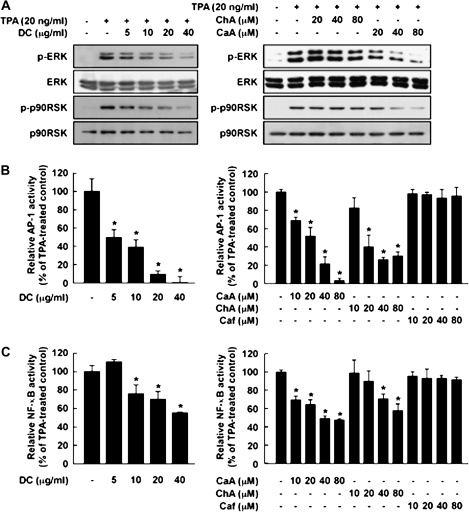
Fig. 4.
Effects of DC, CaA, ChA or Caf on TPA-induced phosphorylation of ERKs or p90RSK or activation of AP-1 and NF-κB in JB6 P+ cells. (A, left) DC or (right) CaA, but not ChA, inhibits TPA-induced phosphorylation of ERKs and p90RSK. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B, left) DC or (right) CaA or ChA, but not Caf, inhibits TPA-induced AP-1 transactivation. (C, left) DC or (right) CaA or ChA, but not Caf, suppresses TPA-induced NF-κB transactivation. AP-1 and NF-κB activities are expressed as percent inhibition relative to cells treated with TPA alone. Data are presented as means ± SDs of AP-1 or NF-κB luciferase activity calculated from three independent experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference between groups treated with TPA and each compound and the group treated with TPA alone (P < 0.05).