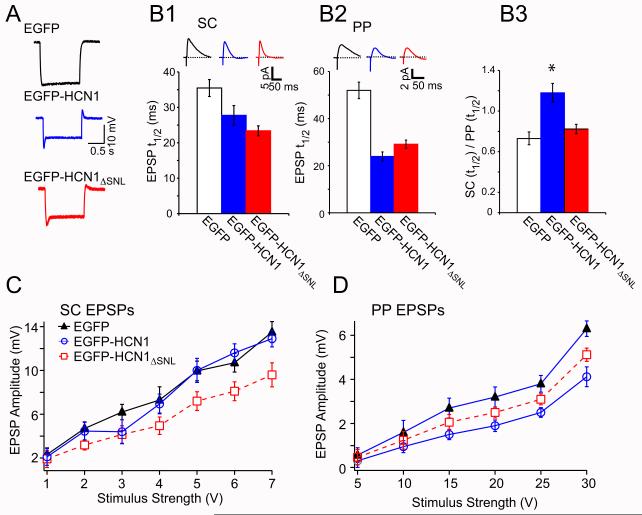
Figure 5. Whole-cell recordings from CA1 neurons expressing EGFP-HCN1 or EGFP-HCN1ΔSNL indicate presence of Ih in intracellular compartments.
A series of electrophysiological properties were determined for CA1 pyramidal neurons from HCN1 KO mice expressing EGFP (control, black), EGFP-HCN1 (blue) or EGFP-HCN1ΔSNL (red). (A) Somatic voltage traces from whole-cell current-clamp recordings showing expression of full-length or truncated HCN1 resulted in a prominent depolarizing voltage sag in response to 100 pA hyperpolarizing current steps from a holding potential of −70 mV. (B) Expression of EGFP-HCN1 and EGFP-HCN1ΔSNL differentially enhanced t1/2 decay time of EPSPs in response to stimulation of proximal (SC) inputs (B1) versus distal (PP) inputs (B2). (B3) Ratio of SC/PP EPSP t1/2 values was significantly different following expression of EGFP-HCN1 versus EGFP-HCN1ΔSNL. Peak amplitude input-output curves for SC (C) and PP (D) EPSPs from CA1 pyramidal neurons expressing EGFP (black triangles), EGFP-HCN1 (blue circles) or EGFP-HCN1ΔSNL (red squares). (Error bars: SEM).