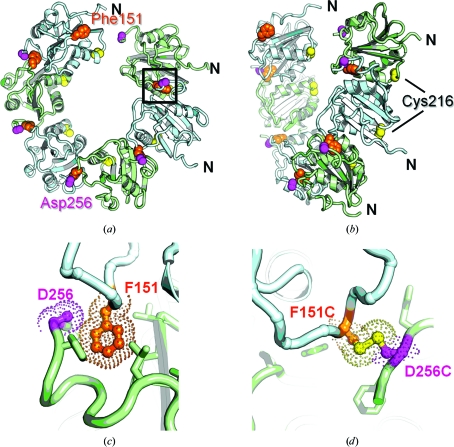
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of the spiral hexamer structure of wt SV40 T-ag OBD shown as a ribbon diagram. (a) This ‘top’ view is looking down the sixfold axis. A close-up view of the area bounded by the black box is shown in (c). (b) This ‘side’ view is rotated ∼90° relative to the view in (a) and clearly shows the ‘gap’. Alternating monomers of T-ag OBD are colored cyan and green, respectively. The residues Phe151, Cys216 and Asp256 are shown as orange, yellow and magenta spheres, respectively. (c) A close-up view of the interface showing Phe151 (orange) and Asp256 (magenta) as sticks. Note that there are no side chains modelled for the Asp256 residue. (d) A molecular model of the disulfide bridge that could form between F151C and D256C. The S atoms are colored yellow.