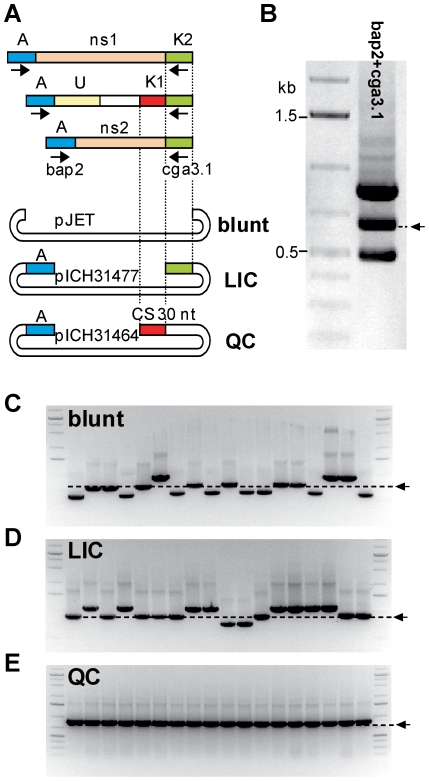
Figure 6. Comparison of blunt-end cloning, ligation-independent cloning and QC cloning using a mix of defined PCR products.
(A) To compare efficiency of the three cloning methods, a mixture of three PCR products, two unspecific (ns1 and ns2) and one immunoglobulin fragment, was cloned (A, adaptor; U, unknown sequence; K, known sequence; ns, non-specific; CS, catching sequence). (B) PCR product mix amplified using primers bap2 pc and cga3.1. The arrow indicates the immunoglobulin fragment. (C, D, E) 12 randomly chosen clones for each cloning strategy were analyzed by colony PCR using vector primers. The immunoglobulin insert size is indicated by an arrow and a dashed line. (C) Unspecific blunt-end cloning into pJET1.2. (D) ligation-independent cloning into pICH31477 using a CS identical to cga3.1. (E) QC cloning into pICH31464.