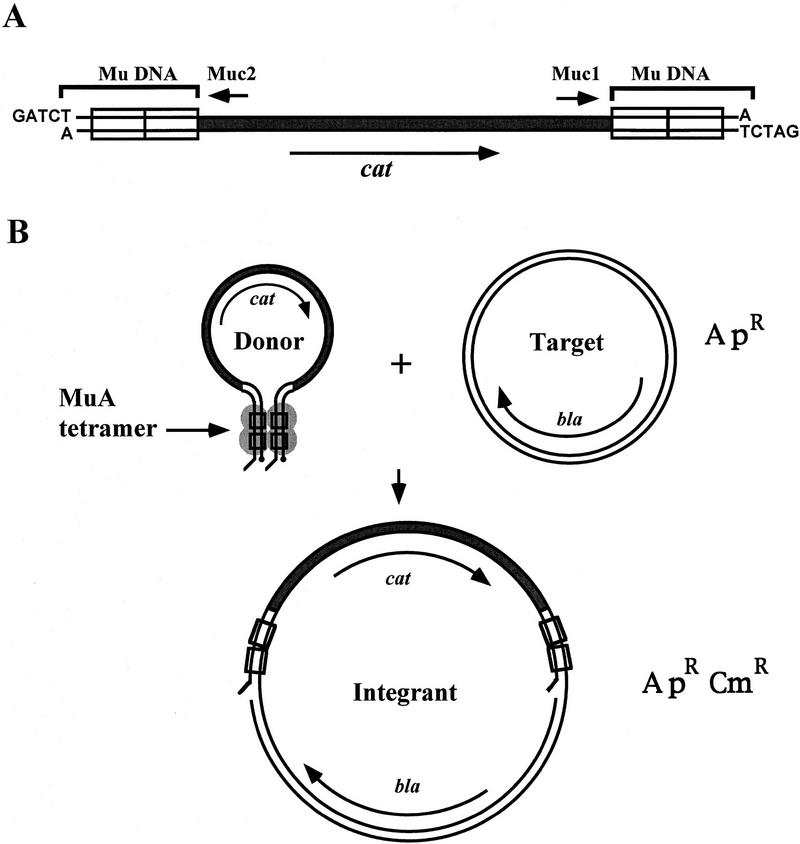
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the utilized in vitro transposition system. (A) cat–Mu minitransposon. The linear transposon fragment is shown to be released from its vector plasmid by BglII digestion; it is therefore in precut configuration. (Rectangles) MuA binding sites; (small arrows) primers used in sequencing. (B) The reaction. MuA forms with the transposon ends a tetrameric transposition complex, a transpososome, that integrates the minitransposon into the target DNA. (ApR, CmR) Ampicillin and chloramphenicol resistance, respectively. (Long arrows) Genes coding for β-lactamase (bla) and CAT (cat); (•) reactive donor DNA 3′ ends.