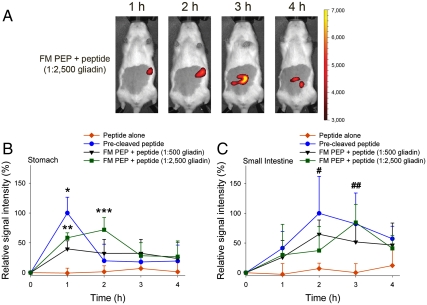
Fig. 5.
Impact of admixed gliadin amount on FM PEP activity. Rats were administered FM PEP by gavage with peptide and gliadin addition at ratios of 1∶500 and 1∶2,500 (PEP∶gliadin, w/w), respectively. (A) Pictures depict the dynamics of the fluorescence signal during 4 h of observation in a representative animal receiving FM PEP + peptide (1∶2,500 gliadin). Color scales are identical. (B, C) Relative fluorescence signal intensity of FM PEP + peptide admixed with gliadin (1∶500 and 1∶2,500, w/w) (B) in the stomach or (C) small intestine compared to oral administration of precleaved peptide or peptide alone. Mean + SD, n = 4–9. *Precleaved peptide (p < 0.01) and **FM PEP + peptide (1∶500 and 1∶2,500 gliadin) (p < 0.05) vs. peptide alone, ***FM + peptide (1∶2,500 gliadin) vs. precleaved peptide and peptide alone, #Precleaved peptide and FM + peptide (1∶500 gliadin) vs. peptide alone, ##Precleaved peptide and FM PEP + peptide (1∶500 and 1∶2,500 gliadin) vs. peptide alone (all p < 0.05).