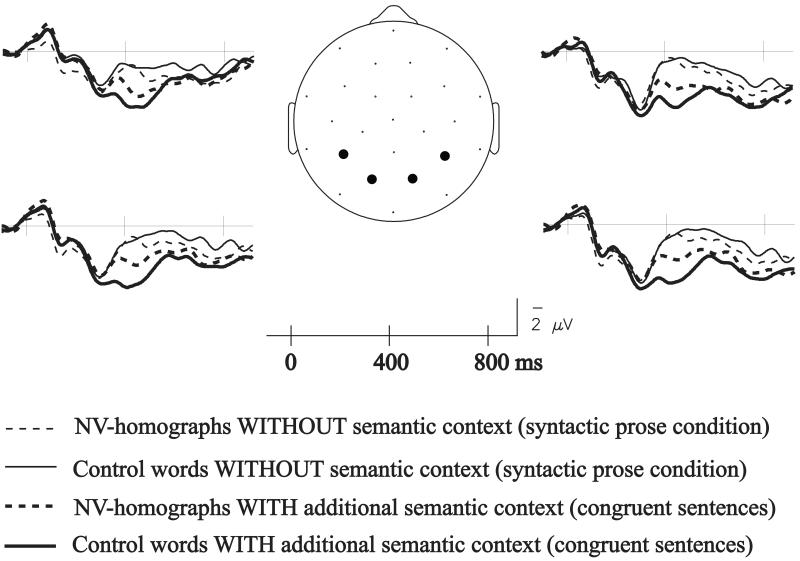
Figure 3.
Grand average ERPs to ambiguous words and unambiguous words in syntactic prose sentences and congruent sentences are overlaid at 4 representative central/posterior electrode sites (LDPa, RDPa, LMOc, and RMOc) to highlight the influence of semantic constraints on the N400. Similar to younger adults’ data pattern, N400 amplitudes to both ambiguous and unambiguous words are highly attenuated (made more positive) in the presence of semantic constraints, although this attenuation is greater for unambiguous than ambiguous targets in cloze-probability matched sentence contexts.